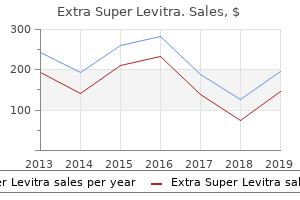
"Order extra super levitra 100mg on line, erectile dysfunction protocol book scam".
By: T. Pyran, M.A., M.D.
Deputy Director, State University of New York Downstate Medical Center College of Medicine
Experimental paradigms that involve signal detection erectile dysfunction doctor in columbus ohio buy cheap extra super levitra on-line, source monitoring or attribution processes erectile dysfunction treatment in thane purchase extra super levitra from india, alone or in combination erectile dysfunction drugs in australia buy cheap extra super levitra on line, have helped to conceptualise hallucinations in cognitive terms (David 2004) and probabilistic reasoning plays some role in delusions (Gilleen & David 2005; Freeman 2007) erectile dysfunction hypnosis cheap 100 mg extra super levitra fast delivery. Negative or deficit symptoms map more easily onto those deficits familiar in neurologically damaged patients. Neuropsychological function has been related to various indices of outcome and predictors of rehabilitation success. Indeed, such functioning is a much stronger predictor of global outcome than symptoms. Vigilance was related to social problem-solving and skill acquisition while card sorting predicted functioning in the community. Structural brain imaging Pathology at the microscopic level is still held up as the defining characteristic of a disease. The reasons are obvious: high-level anatomical information can be gleaned from any and all types of patient; samples can be studied that begin to meet epidemiological standards in terms of representativeness and lack of bias; associations with relevant aetiological factors such as family history, treatment response and phase of illness can all be studied systematically without the need to wait for death and to contend with post-mortem artefacts. Studies of structural neuroimaging in schizophrenia have parallels with neuropsychology. These studies, in demonstrating and indeed quantifying consistently observed effects, will inevitably downgrade findings relating to specific brain structures in individual studies. Hence it remains possible that a particular neuroanatomical structure (or network of structures) deemed key to schizophrenia would nevertheless, because of its size, location or difficulties in measurement, be submerged among the larger effect sizes highlighted by metaanalytic reviews. Nevertheless, the range of values in schizophrenia overlaps considerably with the normal population so this finding has little clinical utility. The same reviewers calculated that the average loss of brain tissue was a mere 3%, with an effect size. If there is a region that seems to attract more tissue loss than the brain as a whole it is the temporal lobes, with around 8% loss on average in the same review. The overall loss of brain volume was 2% and the overall increase in ventricular volume was 26%, mostly accounted for by increase in the body of the lateral ventricles. Medial temporal structures stood out from the rest, with the amygdalae, hippocampi and parahippocampi down by about 6% on both sides; however, this was equivalent to effect sizes (for hippocampus and parahippocampus) of between 0. As well as having larger ventricles, affected twins had smaller temporal lobes and hippocampi than their co-twins. This compelling work confirmed the association between medial temporal volume loss and the schizophrenia phenotype as well as implying a necessary role for non-genetic factors, obstetric complications being a prime suspect (Dalman et al. Subsequent research has shown that unaffected relatives of people with schizophrenia tend to have larger ventricles than non-related controls. The frontal lobes, despite their obvious functional relevance to schizophrenia, do not show quite the same level 84 Chapter 2 of structural loss, with a mean reduction effect size of 0. Most studies have shown that grey matter takes the brunt of volume changes (Zipursky et al. Large white matter tracts such as the corpus callosum are easy to define, especially in the sagittal plane. This has been shown to be reduced in size in a small meta-analysis (Woodruff et al. Voxel-based methods of analysis avoid the difficulty (and tedium) of tracing around predetermined anatomical regions and are increasingly being employed in structural neuroimaging research. When used in schizophrenia, both white and grey matter regions (medial temporal lobe again, plus insula and prefrontal regions) may be identified as having reduced density, which probably translates to reduced volume (Shapleske et al. In contrast to the repeated finding of reduced cerebral volume, the striatum (particularly the caudate) has been found to be increased in size. Now there has been an upsurge of interest in neuropathology, fuelled in part by the findings from neuroimaging and molecular biology (Harrison 1999; Harrison & Weinberger 2005). The coexistence of brain lesions or pathology in people Left (a) Right 69 57 (b) 43 31 21 15 11 7. In row (a), left and right whole-brain threedimensional images are overlaid with all regions in which significant volume deficits in patients with schizophrenia were reported.
Additional recommendations to minimize the possibility of biasing feedback to the witness include requiring that the officer read instructions to the witness from a pre-printed form erectile dysfunction caused by spinal cord injury purchase extra super levitra 100 mg with amex. Based upon information presented to the committee impotence new relationship discount 100mg extra super levitra otc, it appears that police departments do not always document identification procedures in instances when an identification is not made erectile dysfunction and causes purchase extra super levitra 100mg line. Further erectile dysfunction young cure purchase extra super levitra 100 mg fast delivery, if a witness does make an identification, practices differ as to how such information is documented and preserved. Some agencies, for example, require officers to document this information in a written report. Fillers are selected for their physical similarities to the suspect (gender, race, hair length and color, facial hair, height, skin tone, and other distinguishing features). Traditionally, the suspect and fillers are seated or stood in a row, and the witness views the lineup from behind a two-way mirror. Live lineups are used in some jurisdictions, but they are not the predominant method used by law enforcement. First, in certain circumstances, legal counsel may be required at a lineup, thereby making it less attractive to police and prosecutors. Second, in smaller jurisdictions, it may be difficult to obtain suitable fillers. This evidence has influenced how scientists carry out their experiments, resulting in the use of blind or double-blind procedures to control for this form of bias. Blind assessmentb has been used since the late 18th century; an early medical trial in 1835 used double-blind assessment, and psychologists started using blinding in the 20th century. In single-blind experiments, participants do not know which treatment they are receiving; this form of blinding is used widely across scientific fields. In experiments involving humans, as in medical or psychological research, double-blind procedures are used to guard against "expectancy effects" for both participants and researchers. In a classic double-blind clinical trial, some patients receive active medication and others are given an alternative (either a "standard treatment" or a similar-looking placebo without active ingredients), but neither researchers nor participants know who is receiving which treatment. In an eyewitness identification setting, double-blinding can be used to prevent a lineup administrator from either intentionally or unintentionally influencing a witness. In these cases, neither the eyewitness nor the administrator knows which persons in a photo array or live lineup are the suspected culprits and which are the fillers. In a double-blind photo array, the officer or detective conducting the investigation reads a set of standard instructions to the witness. The instructions may include an advisory that the officer about to show the photos does not know whether any of the photos are of the person who committed the crime. The officer then leaves the room and a second officer-perhaps a patrol officer-displays the physical similarities to the suspect). Third, conducting a lineup requires a significant amount of time and labor, 17 thereby making photo arrays a more attractive alternative that may be undertaken promptly and with less demand on department resources. It is the duty of this second officer (the "blind administrator") to show the photos and, if an identification is made, document what the witness said and ask the witness how certain she or he is of their identification. Once all photos have been shown, the officer reports the result of the procedure to the investigating officer (preferably out of earshot from the witness). As an alternative to a double-blind array, some departments use "blinded" procedures. A blinded procedure prevents an officer from knowing when the witness is viewing a photo of the suspect, but can be conducted by the investigating officer. A photograph of a filler is placed in the top folder, and a photograph of the suspect and four additional fillers are placed in the next five folders. The six folders are then shuffled so that the officer does not know which folder contains the image of the suspect. Two folders with blank paper are placed on the bottom of the stack so that the witness is led to believe that there are more than six images in the array (this is referred to as back-loading, and it prevents the witness from knowing when she or he is about to view the last photograph). The cover of the folder blocks the officer from viewing the photo that the witness is viewing. Rosenthal, Experimenter Effects in Behavioral Research (New York: John Wiley, 1976).
When people are in the promotion focus system erectile dysfunction freedom book extra super levitra 100 mg low price, they experience cheerfulness-related emotions after success erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy treatment options purchase 100mg extra super levitra free shipping. This is true whether people are in a promotion focus from a chronic predisposition to be in that system or from a current situation activating that system erectile dysfunction treatment diabetes discount extra super levitra 100mg line. The pleasure of success and the pain of failure are different in the prevention focus system erectile dysfunction caused by hernia buy extra super levitra 100mg with visa. These emotional differences between promotion and prevention also apply to emotional 432 appraisals. Individuals in a promotion focus more readily appraise objects and events along a cheerfulness-dejection dimension, whereas individuals in a prevention focus more readily appraise objects and events along a quiescence-agitation dimension. Regulatory focus theory is especially concerned with the differences between promotion and prevention motivationally. Regulatory focus theory proposes that when people pursue goals, their strategic preferences are different in a promotion versus a prevention focus. Individuals in a promotion focus experience positive and negative events in the world as gains and nongains, respectively, because their concerns are about accomplishments and aspirations. Strategic eagerness is also about ensuring gains and not wanting to miss gains, so eagerness fits a promotion focus. In contrast, individuals in a prevention focus experience positive and negative events in the world as nonlosses and losses, respectively, because their concerns are about safety and meeting obligations. Strategic vigilance is also about trying to be careful to ensure nonlosses and not wanting to commit mistakes that produce a loss, so vigilance fits a prevention focus. Indeed, many studies have found that individuals in a promotion focus prefer to use eager strategies to pursue goals, whereas individuals in a prevention focus prefer to use vigilant strategies. There is also evidence that when an eager versus strategic approach to an achievement task is experimentally manipulated, individuals in a promotion focus perform better when instructed to use eager means than when instructed to use vigilant means, whereas the opposite is true for individuals in a prevention focus. Persuasive regulatory focus theory messages with an eager tone are more effective in changing attitudes when received by individuals in a promotion than a prevention focus, whereas the reverse is true for persuasive messages with a vigilant tone. The difference between a promotion focus on eager gains versus a prevention focus on vigilant nonlosses also influences the nature of ingroup versus out-group bias. For individuals in a promotion focus, in-group members are treated with a positive bias ("promoting us"), but there is little bias regarding outgroup members. In contrast, for individuals in a prevention focus, the out-group members are treated with a negative bias ("preventing them"), but there is little bias regarding ingroup members. Because of this difference in strategic preferences for people in a promotion versus a prevention focus, the motivational significance of success and failure is also very different in promotion versus prevention. When individuals succeed in a promotion focus, that increases their eagerness (experienced as high-intensity joy), and when they fail, that decreases their eagerness (experienced as low-intensity sadness). In contrast, when individuals succeed in a prevention focus, that reduces their vigilance (experienced as low-intensity calmness), and when they fail, that increases their vigilance (experienced as high-intensity nervousness). This regulatory focus difference in the motivational significance of success and failure influences postperformance expectations as well. Thus, after success on an initial trial of a task, individuals in a promotion state, more than individuals in a prevention state, should raise their expectations for the next trial (be optimistic) to maintain the strategic eagerness that sustains their focus. After failure on an initial trial, individuals in a prevention state, more than individuals in a promotion state, should lower their expectations for the next trial (be defensively pessimistic) to maintain the strategic vigilance that sustains their focus. Regulatory focus differences in strategic approaches are especially likely to be revealed when there is a conflict between different choices or different ways to proceed on a task. One prevalent conflict is between being "risky" or being "conservative" when making a judgment or decision. When people are uncertain, they can take a chance and treat something as being correct that could actually be incorrect (a possible error of commission).
The onset of fixed dystonia occurred after a peripheral injury in 68% of cases (compared with 5% in the control group) and 44% of patients had associated features of complex regional pain syndrome (reflex sympathetic dystrophy) erectile dysfunction statistics worldwide extra super levitra 100 mg without prescription. The authors conclude that fixed dystonia commonly occurs after peripheral injury and overlaps with complex regional pain syndrome erectile dysfunction drugs on nhs order extra super levitra canada. The study provides compelling evidence that this syndrome has a psychogenic basis in the majority of patients erectile dysfunction causes diabetes discount extra super levitra 100mg visa. The presence of a psychiatric history is often cited as evidence in favour of a psychogenic origin for the presenting movement disorder erectile dysfunction support group extra super levitra 100 mg mastercard. Distraction tasks include asking the patient to perform tests of mental concentration. A slower (3 Hz) rhythm may be a more sensitive test than faster rhythms A load (weight or pressure) is applied to the affected limb. Organic tremor tends to diminish whereas functional tremor may increase in amplitude. In this situation increased load triggers physiological clonus As above Psychogenic myoclonus may be triggered by a variety of stimuli. The delay is also usually longer than seen in stimulus-sensitive organic myoclonus Specific caveat 795 All movement disorders vary to some degree and will often worsen with anxiety Organic disorders may be susceptible to attentional factors to a minor degree Entrainment Coactivation Dystonia Myoclonus Distraction Variability in stimulus response * In each case a negative test does not exclude a psychogenic basis for the disorder. The lifetime prevalence rates for the most common comorbid diagnoses were 43% for major depression, 38% for anxiety disorders, and 28. Personality disorders were identified in 45%, and 38% had prominent features of other medically unexplained symptoms. Almost all reporting of scans is currently based on qualitative assessment and in clinical settings the extent of false negatives and positives will undoubtedly vary between centres. Electromyography can be used to verify some of the characteristics of psychogenic tremor and myoclonus listed in Table 12. However, the sensitivity and specificity of these techniques has yet to be established. Combined electroencephalographic and electromyographic recordings may be helpful in assessing myoclonus. The demonstration of a prolonged pre-movement Bereitschaftspotential is good evidence of a psychogenic basis but this may be attenuated or even absent in healthy subjects under certain conditions (Terada et al. Furthermore, this technique requires back-averaging of multiple events, which may be impractical if the jerks occur infrequently. However, there is considerable overlap between different somatoform presentations (Wessely et al. Onset after minor physical injury is common and much more frequently reported than onset after a psychological trauma (Factor et al. In the first, the movements are essentially construed simply as arising from voluntary-like activity. The second mechanism involves cocontraction of normally opposing agonist/antagonist muscle groups. In this case tremor arises through physiological clonus, as seen in shivering or with prolonged tonic muscular exertion. These authors commented on a strong tendency for initial symptoms to be replaced or joined by new ones. Principles and techniques that have proven useful in other somatoform conditions are likely to be of benefit, although many have yet to be fully evaluated. Cognitive behavioural therapy is a well-established treatment for a variety of somatoform disorders (Kroenke & Swindle 2000), but other forms of psychotherapy may be preferable for some patients. A multidisciplinary approach combining psychotherapy with physiotherapy and other rehabilitation services has been recommended but again requires evaluation (Schrag et al. An impressive 52% were felt to have benefited significantly from treatment, with complete resolution of symptoms in 25%; 35% of patients returned to employment. A less optimistic view comes from the most detailed study to date by Feinstein et al. These authors describe outcome in 42 patients (from a series of 88) followed up after a mean interval of 3. Symptoms had improved in one-third of the patients but were the same or worse in over half. Poor outcome was associated with long duration of symptoms at initial presentation, gradual onset and by the presence of psychiatric comorbidity.
Discount 100mg extra super levitra with visa. Impotence & Erectile Dysfunction - In Fit & Healthy Younger Men.