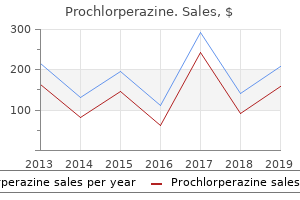
"Prochlorperazine 5 mg amex, everlast my medicine".
By: P. Abe, M.A.S., M.D.
Co-Director, Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine
In examining the differences in physiology between islets from mice exposed to Cd vs control mice administering medications 6th edition buy 5 mg prochlorperazine with visa, we found a lower ratio of insulin to proinsulin treatment resistant anxiety best prochlorperazine 5 mg, pointing towards an impairment in normal insulin processing symptoms 3 weeks into pregnancy order 5 mg prochlorperazine overnight delivery. Edwards Diabetes is a devastating metabolic disease projected to afflict 693 million individuals worldwide by the year 2045 treatment vs cure purchase genuine prochlorperazine. While caloric excess, physical inactivity, and genetic susceptibility all contribute to disease risk, these factors alone fail to fully account for the magnitude of the epidemic. Arsenic has been shown to disrupt the key pathways regulating glucose homeostasis, namely insulin secretion and insulin action, resulting in glucose intolerance in animal models. These effects are corroborated by epidemiological evidence suggesting that arsenic exposure is associated with diabetes in human populations. Moreover, selenium-containing proteins (selenoproteins) have biological functions that are predicted to antagonize various aspects of arsenic toxicity. Body weight regulation and composition, glucose tolerance, and insulin secretion were examined. Disruptions in either dietary selenium content and/or selenoprotein deficiency altered arsenic-induced effects on body composition and insulin secretion. These data suggest that selenium/ selenoproteins have mitigating role in arsenic-induced metabolic toxicity. Ongoing studies seek to define the specific selenoproteins mediating arsenic toxicity in order to both clarify the underlying mechanisms by which these factors preserve metabolic health as well as to identify populations who may be at enhanced risk of metabolic dysfunction from arsenic exposure. The progression of chronic kidney disease (prevalence > 3% of adult population) to end-stage renal disease is a source of considerable morbidity and mortality in western populations. While pathological processes of the glomerulus are known to play a major role in this disease, it is the demise of the renal tubules, predominantly the proximal tubule, that is the major correlate to the progression to end-stage disease. Though diabetes is the largest contributor to this disease, the heavy metal cadmium is increasingly appreciated as a significant etiological factor, and with respect to this metal, the proximal tubule is the main target site for renal toxicity. Proximal tubule cells are also a major site for glucose toxicity due to the major role of the proximal tubule in glucose reabsorption. During hyperglycemia, the proximal tubule-glucose load increases and potentially saturates the reabsorption process eventually leading to the accumulation of sorbitol, a toxic metabolic side-product of glucose, produced through the reduction of the aldehyde group by aldose reductases. Since the exposure and accumulation of cadmium in the proximal tubule cells occurs throughout the human population, the development of chronic kidney disease occurs with a high base line of metal exposure, thus the development of this disease most likely occurs through and interaction or collaboration of these two agents. We recently discovered that an isoform of aldose reductase is induced by cadmium exposure and we are now investigating the contribution of this enzyme to glucose-induced sorbitol accumulation and toxicity. Exposures to the glucose can also lead to a loss of epithelial character having similarities to the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, a process that might contribute to the interstitial fibrotic process seen in this disease. We have been characterizing this process, with respect to both morphology and gene expression. It can be appreciated that multiple factors contribute to toxicity and disease processes, and with respect to the kidney, cadmium and hyperglycemic glucose concentrations are two agents that can initiate and accelerate chronic kidney disease. To address these risks, a risk mitigation and management plan should be built already at very early development stages, using a combination of in silico, in vitro, and in vivo approaches. Once chemistry has been initiated, evaluation of activities towards secondary targets (off target pharmacological profiling) that can be associated with undesirable effects needs to be implemented to ensure sufficient compound selectivity. Safety issues affecting other organs, tissues or systems, such as the liver, kidney, immune, gastro-intestinal or nervous systems are less commonly addressed during early drug development. Experiments to understand the mechanisms underlying toxicity are critical to guide chemistry and rank compounds. Examples will be provided to demonstrate the impact and benefit of such investigative safety strategies on drug development. Ultimately, understanding the predictive value of non-clinical safety testing and its translatability to humans will enable us to optimize assays, guide chemistry, and refine strategies in order to address the key safety challenges of the drug discovery process. This approach enables development of drugs that have an acceptable benefit-risk ratio and will deliver the best medicines to patients. W 1058 Reduced Kupffer Cell Clearance Is Causing Elevation of Serum Toxicity Biomarkers in Rat and Monkey in Absence of Organ Injury F. Enzymatic serum biomarkers use to monitor drug safety in preclinical and clinical studies are sometimes not matching actual drug-induced organ injuries. W 1056 Pharmaceutical Investigative Toxicology: Case Studies in Optimizing Drug Discovery and Guiding Human Risk Assessment C. Moving toxicological studies into earlier phases of the research and development chain prevents drug candidates with a safety risk from entering clinical development.
Warmer temperatures could also increase the incidence of disease both by increasing the vector population size and distribution and by increasing the duration of the season in which infectious vector species are present in the environment treatment zinc deficiency best 5 mg prochlorperazine. Many newly emerging infectious diseases arise in tropical regions where the warm temperatures suit the lifecycles of both pathogen and vector 86 treatment ideas practical strategies generic prochlorperazine 5 mg visa. Climate change can increase or decrease the incidence of the insect-transmitted Chagas disease symptoms rectal cancer generic 5 mg prochlorperazine overnight delivery, sand-fly transmitted leishmaniasis chi royal treatment generic prochlorperazine 5 mg free shipping, and other vector-borne and zoonotic diseases, generally with greater illness occurring at higher degrees of warming. Degradation of the permafrost can expose historic burial grounds, enabling the revival of deadly infections from the past. Extended growing periods and expanded habitats are providing some zoonotic pathogens and their vectors with more favourable living conditions. Thus, it cannot always be assumed that the modernization of food value chains will reduce risk. Moreover, especially in low- and middleincome countries, people are consuming more animal-source foods than in the past, which results in potential exposure to pathogens, including zoonotic pathogens. Climate change Many zoonoses are climate sensitive and a number of them will thrive in a warmer, wetter, more disasterprone world foreseen in future scenarios. Pathogens that are widely distributed, mutate rapidly and are multi-host are considered most likely to jump species. Pathogens that spread using the respiratory functions of the host (which are over-represented among emerging diseases) have fewer barriers to moving from one host to another than pathogens spread via other routes. Certain animals, in their turn, are more likely to harbour zoonotic or potentially zoonotic pathogens based on their physiological characteristics, ecosystem niche, social behaviour and relatedness to humans. Some studies detected higher numbers of zoonotic viruses in animal species that have become abundant and have expanded their range by adapting to human-dominated landscapes. However, as with all animals, they are not risks in and of themselves, and it is only when there is close contact with people that there is the potential for this risk to be realized. Baby owls in a cage sold in an animal market in Yogyakarta, Indonesia Photo credit: Ibenk 88 / Shutterstock. The section starts with some background on coronaviruses and continues from the One Health perspective, reflecting both veterinary and medical experiences and commonalities between important coronavirus diseases and pandemics. To date, there have been around 2,500 laboratory confirmed cases mostly human to human, of which more than one third proved fatal. Sporadic cases continue to occur as the infection remains present in dromedary camels. Other research has shown the virus to be 96 per cent identical to a previously identified bat coronavirus, with a common ancestor about 50 years ago. Coronaviruses are a large group of viruses that infect many animals and humans and are responsible for numerous diseases. They are named "corona" for the crown-like arrangement of the spike-shaped proteins on the surface of their membranes. Some human coronaviruses usually cause mild upper respiratory illness like the common cold. They can also cause serious diseases such as infectious peritonitis in cats and respiratory and enteric infections in cattle. In addition to these well-known, sporadic, locally important and long-established diseases, there have been at least six major outbreaks of novel coronaviruses in the last century, all of which imposed high costs across several continents: 1. It emerged in the 1930s and is still one of the main causes of economic losses in the poultry industry, with repeated waves of disease caused by different strains. Since then different strains have caused waves of disease in Asia, Europe and the Americas. The illness then spread to more than two dozen countries in North America, South America, Europe and Asia before it 6. The Coronavirinae subfamily comprises four genera: Alphacoronavirus Alphacoronaviruses cause respiratory tract illnesses and common colds in humans, and gastroenteritis in animals. Gammacoronavirus They infect mainly avian species and sometimes mammals including cetaceans.
Generic prochlorperazine 5mg mastercard. Improving Daily Symptom Management for Patients with MS.
Classicpathway For many years this was the only way in which complement was known to be activated symptoms breast cancer purchase generic prochlorperazine on line. Ig IgM and some subclasses of IgG (in the human medicine hat lodge generic prochlorperazine 5 mg on line, IgG1IgG3) treatments order prochlorperazine australia, when bound to antigen are recognized by Clq to initiate the classic pathway treatment jellyfish sting discount prochlorperazine 5 mg with amex. C4b then binds to C2, and also, via a very unusual type of reactive thioester bond, to any local macromolecule, such as the antigen antibody complex itself, or to the membrane in the case of a cell-bound antigen. It has both structural and functional similarities to C2, and both are coded for by genes within the very important major histocompatibility complex (see Fig. Lyticpathway Lysis of cells is probably the least vital of the complement reactions, but one of the easiest to study. It is initiated by the splitting of C5 by one of its two convertases: C3bC2aC4b (classic pathway) or C3b BbPr (alternative pathway). Needless to say, some bacteria have evolved various strategies for avoiding this (see Fig. Complementinhibitors In order to prevent over-activation of the complement cascade, there are numerous inhibitory mechanisms regulating complement. Yet others destabilize the molecular complexes that build up during complement activation. Alternativepathway the principal features distinguishing this from the classic pathway are the lack of dependence on calcium ions and the lack of need for C1, C2 or C4, and therefore for specific antigenantibody interaction. In this simplified scheme, which should be read from left to right, are shown the effects of injury to tissues (top left) and to blood vessels (bottom left). The small black rods represent bacterial infection, a very common cause of inflammation and of course a frequent accompaniment of injury. Note the central role of permeability of the vascular endothelium in allowing access of blood cells and serum components (lower half) to the tissues (upper half), which also accounts for the main symptoms of inflammation redness, warmth, swelling and pain. Further details of the role of antibody and lymphocytes in inflammation can be found in Figs 3439. If for any reason inflammation does not die down within a matter of days, it may become chronic, and here the macrophage and the T lymphocyte have dominant roles (see Fig. Mast cell A large tissue cell with basophilic granules containing vasoactive amines and heparin. It degranulates readily in response to injury by trauma, heat, ultraviolet light, etc. Kinin system A series of serum peptides sequentially activated to cause vasodilatation and increased permeability. C3a and C5a these stimulate release by mast cells of their vasoactive amines, and are known as anaphylatoxins. It binds to phosphorylcholine, which is found on the surface of many bacteria, fixes complement and promotes phagocytosis; thus it may have an antibody-like role in some bacterial infections. This acute-phase response can be viewed as a rapid, not very specific, attempt to deal with more or less any type of infection or damage. Inflammatory cytokines the inflammatory response is orchestrated by several cytokines, which are produced by a variety of cell types. They also induce the acute phase response and, later, the process of tissue repair. Chemokines these are a very large family of small polypeptides, which have a key role in chemotaxis and the regulation of leucocyte trafficking. There are two main classes of chemokines, based on the distribution of conserved disulphide bonds. They bind to an equally large family of chemokine receptors, and the biology of the system is further complicated by the fact that many of the chemokines have multiple functions, and can bind to many different receptors. They shot to prominence when it was discovered that some of the chemokine receptors. These changes, together with the selective local release of chemokines, regulate the changes in cell traffic that underlie all inflammatory responses.
A scoring system to predict renal outcome in IgA nephropathy: a nationwide 10-year prospective cohort study symptoms zollinger ellison syndrome order 5mg prochlorperazine with mastercard. Clinical decision support system for end-stage kidney disease risk estimation in IgA nephropathy patients medications via ng tube purchase prochlorperazine line. A scoring system to predict renal outcome in IgA nephropathy: from a nationwide prospective study symptoms estrogen dominance 5mg prochlorperazine otc. Development and validation of a prediction rule using the Oxford classification in IgA nephropathy treatment leukemia cheap prochlorperazine 5 mg without a prescription. Progression of chronic kidney disease: the role of blood pressure control, proteinuria, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition: a patient-level meta-analysis. Effects of intensive blood pressure lowering on cardiovascular and renal outcomes: updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Low-dose combination therapy with temocapril and losartan reduces proteinuria in normotensive patients with immunoglobulin a nephropathy. The effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor on IgA nephropathy and the influencing factors. Zhonghua nei ke za zhi [Chinese journal of internal medicine] 41(6):399403, 2002 2002; 41: 399-403. Validation of the Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy in cohorts with different presentations and treatments. Long-term renal survival and related risk factors in patients with IgA nephropathy: results from a cohort of 1155 cases in a Chinese adult population. Early Change in Urine Protein as a Surrogate End Point in Studies of IgA Nephropathy: An Individual-Patient Meta-analysis. Antiproteinuric effect of angiotensin receptor blockers in normotensive patients with proteinuria: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. The effect of profilactic prednisolon therapy on renal involvement in henoch schonlein vasculitis [abstract]. Effectiveness of early prednisone treatment in preventing the development of nephropathy in anaphylactoid purpura. Early prednisone therapy in Henoch-Schonlein purpura: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rituximab treatment for chronic steroid-dependent HenochSchonlein purpura: 8 cases and a review of the literature. Brief Report: Rituximab for the Treatment of Adult-Onset IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein). Antiphospholipase A(2) receptor autoantibodies: a comparison of three different immunoassays for the diagnosis of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Noninvasive diagnosis of primary membranous nephropathy using phospholipase A2 receptor antibodies. Phospholipase A2 Receptor 1 Epitope Spreading at Baseline Predicts Reduced Likelihood of Remission of Membranous Nephropathy. Predicting chronic renal insufficiency in idiopathic membranous glomerulonephritis. Prognostic value of risk score and urinary markers in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibody titer and subclass in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Cancer risk after cyclophosphamide treatment in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Oral cyclophosphamide versus chlorambucil in the treatment of patients with membranous nephropathy and renal insufficiency. Methyl prednisolone plus chlorambucil as compared with prednisolone alone for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy - a preliminary study. A randomized, controlled trial of steroids and cyclophosphamide in adults with nephrotic syndrome caused by idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Comparison of immunosuppressive therapeutic regimens in patients with nephrotic syndrome due to idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Controlled trial of methylprednisolone and chlorambucil in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Controlled trial of monthly alternated courses of steroid and chlorambucil in idiopathic membranous nephropathy.