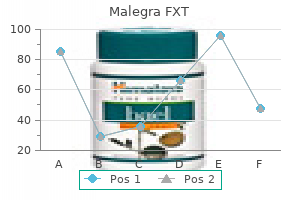
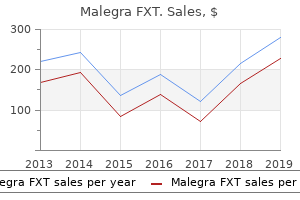
"Buy malegra fxt online now, erectile dysfunction reasons".
By: Q. Ateras, M.A.S., M.D.
Professor, Emory University School of Medicine
Do measure the body temperature at the scene of death or soon thereafter before the body is refrigerated impotence pronunciation cheap 140mg malegra fxt. Determination of the rectal temperature may be made dt the scene; temperature of the liver can be determined as soon as the body is opened erectile dysfunction and diabetes type 2 discount malegra fxt 140 mg with visa, or by means of a small incision over the liver area upon arrival of the body at the morgue impotence male buy 140mg malegra fxt otc. The weather bureau can supply data regarding temperature erectile dysfunction without pills buy malegra fxt overnight delivery, humidity, wind velocity, cloud cover, etc. All of these data must be interpreted with regard to the environment where the body was exposed. Temperature, air movement, radiant heat bodies, moisture, etc, must be noted at the scene. New Engl J Med 224:281-288, 1941 1Editors note: During hot summer weather there is a rapid rise in temperature in the passenger compartment and trunk of automobiles left exposed to the sun. This rapid temperature rise may easily cause the death of small children ~/nd animals left unattended in the automobile while the parent shops. This is unfortunate because competent and skillful examination of this area is absolutely essential in medicolegal autopsies. Injuries inflicted by cutting, stabbing, and firearms are omitted from the discussion which follows. The presence or absence of externally visible cutaneous injuries and their appearance are determined by the amount~ of force applied, rate and duration of application of force, and the surface area involved in energy transfer. The smaller the area of application of force, the more likely it is to produce nonuniform, injurious displacement of tissues. The longer a compressing ligature remains on the neck, the more likely it is to produce a permanent furrow. Hanging usually leaves an inclined furrow on the neck which duplicates the size and pattern of the rope (electrical cord, belt, etc. Ordinarily the furrow is situated above the level of the thyroid cartilage, rises to a suspension point at the occiput or posterior D 119 D aspect of the neck, and has its low point 180 degrees opposite the suspension point. The cause of death by hanging, in most instances, is compression of the cervical vasculature and not asphyxia by airway obstruction. If this compression halts venous return from the head for an appreciable interval prior to cessation of arterial flow to the head, it causes intense venous engorgement above the level of the ligature with petechiae of the eyelids and conjuctivae. When arterial flow is obstructed rapidly by the compressing force, the former findings are absent and death results from cerebral isehemia. Characteristically there is minimal or no hemorrhage in the cervical soft tissues, and fractures of the laryngeal cartilages or hyoid bone do not occur in a typical hanging. Fracture of the rostral cervical vertebral column is the "objective" of a judicial hanging and occurs only as a result of a properly placed noose and a drop of sufficient length (based upon body weight) to cause fracture but not decapitation. The external stigmata produced by ligature strangulation are determined by the same variables enumerated above. The most important distinctions from a hanging furrow are that the mark of a ligature strangulation is oriented horizontally on the neck, does not rise to a suspension point, and usually is situated below the level of the thyroid cartilage. In the majority of instances, it is more severe than that caused by hanging and less severe than that produced by manual strangulation (see below). This requires that the ligature be knotted or otherwise fastened so that cervical compression is maintained following loss of consciousness. Manual strangulation typically is characterized by the presence of small contusions and abrasions in groups on the front and back of the neck. Petechiae of the eyelids and conjunctivae are frequently, but not invariably present. Internal cervical hemorrhage is the rule in manual strangulation, and fractures of the hyoid bone or laryngeal cartilages, or both, are common. However, there may be no fractures, particularly when the victim is young and has considerable elasticity of the latter structures. In these situations, the fractured margins are driven inward (hinged toward the outside), whereas in manual strangulation squeezing of the sides of the hyoid bone and larynx causes the fractured margins to point outward (hinged toward the inside).
The more intense and sophisticated the scrutiny erectile dysfunction young adults purchase malegra fxt 140 mg with mastercard, the fewer the cases that can be classified as instantaneous physiologic deaths injections for erectile dysfunction forum buy 140 mg malegra fxt otc. In order to apply the label impotence at 19 malegra fxt 140 mg cheap, instantaneous physiologic death erectile dysfunction treatment new orleans buy malegra fxt once a day, an intact body with little decomposition must have been available for examination. Without this, the ultimate application of the label "instantaneous physiologic death" is no more than guess work. Table I is a general guide to those procedures of elimination which should be applied in every instance. Before the use of the term instantaneous physiologic death is considered, all of the procedures listed in Table I should have been applied, and no positive findings of significance should have resulted. After the death has been thoroughly investigated, eliminating all apparent causes of death, then some attempt must be made to find "historical" clues which might suggest instantaneous physiologic death. Vasovagal reflex (inhibition) In this situation, a history of a precipitating event will be developed and possibly a history of vasovagal episodes of lesser degree may be elicited from relatives and friends of the deceased. Since the flood of reflex activity of this nature is initiated by an "external cause," the precipitating event (if the death was witnessed) will likely be recalled. Ventricular fibrilation No precipitating event is necessary although there may be one. Such may have occurred when the individual was very tired and under great emotional strain. A combination of the two, vasovagal reflex and ventricular fibrillation, may be possible in theory and may actually take place. But in such an instance, a disease process would be noted at the time of autopsy, and the diagnosis of instantaneous physiologic death would be unnecessary. The type of the instantaneous physiologic death m a y be well enough defined so as to state on the death certificate: 1. Fatal ventricular fibrillation (when there is a history of preceding syncope due to arrhythmia). M a n y d e a t h s, h o w ever, are not witnessed, a n d despite a negative autopsy, etc. I f y o u desire s o m e fascinating reading the following b i b l i o g r a p h y is offered as an i n t r o d u c t i o n. None Cause None Precipitating present* Precipitating present* None Certification tendency to certify: 2. Minor cardiac "cause of death-undetermined" tendency to certify: "death due to diseasem natural causes" D 4. Minor cardiac * May be pressure to put precipitating cause on the death certificate and certify as an accident An overview of different methods (philosophies) of certifying the cause of death in instances where disease is absent or present in minimal (apparently sublethal) amounts. Brod, J, Fencl, V, Hejl, Z, et al: Circulatory changes underlying blood pressure elevation during acute emotional stress (mental arithmetic) in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Simonson, E, Baker, C, "Burns, N, et al: Cardiovascular stress (electrocardiographic changes) produced by driving an automobile. This syndrome claims approximately three babies of every 1,000 live births, with a slight preponderance of males and a higher frequency occurring in lower socioeconomic groups. The peak incidence is in ages 2 to 4 months and 75 percent of the deaths are of infants less than 6 months old. These deaths occur throughout the year but usually are more frequently recorded during the cold months. The majority of victims are found, in a prone position, in their cribs in the morning. Apparently they die rapidly during sleep and do not cry or have audible respiratory distress. Almost half of them have had a minor upper respiratory infection ("cold" or "sniffles") in the week or two preceding death. Typically, they are robust, well-fed, clean infants who appear to be entirely normal prior to their unanticipated deaths.
The typical anatomic features of classic asplenia syndrome are trilobed lungs with bilateral minor fissures and eparterial bronchi xarelto erectile dysfunction 140mg malegra fxt with amex, bilateral systemic atria erectile dysfunction at age 50 order malegra fxt us, midline liver erectile dysfunction best pills order malegra fxt 140 mg, absent spleen impotence versus erectile dysfunction discount malegra fxt 140 mg without a prescription, and variable location of the stomach. Scintigraphy is the standard examination in documenting the absence of the spleen. Congenital Abnormalities, Splenic Asymmetric Density An asymmetry of the glandular breast tissue, visible mammographically on two views. Asymmetry is common but should be evaluated as uncommonly there may be an underlying mass or architectural distortion. Carcinoma, Breast, Imaging Mammography, Primary Signs Asplenia Syndrome Asplenia syndrome is characterized by asplenia, or absence of the spleen, associated with abdominal situs ambiguous. The syndrome is most frequently encountered in males and is associated with severe cyanotic congenital heart diseases. The typical anatomic features of classic asplenia syndrome are trilobar lungs with bilateral minor fissures and epiarterial bronchi, bilateral systemic atria, midline liver, absent spleen, and variable location of the stomach. The term refers to the region and amount of lung that is collapsed or to the underlying pathophysiology. Osteonecrosis in Adults There are various pathological mechanisms causing atelectasis: 1. Postobstruction or resorption atelectasis: the intraalveolar air is resorbed distal to a bronchial obstruction. Figure 1 Patient with obstruction (resorption) atelectasis due to a large central mucous plug. The lung collapse seen with a pneumothorax is also described as relaxation atelectasis. Cicatrization atelectasis, focal or more diffuse collapse resulting from fibrosis or scarring. It is frequently associated with bronchiectasis and also seen in granulomatous diseases. A rounded atelectasis (synonym: folded lung, atelectatic pseudotumor) represents a compression atelectasis seen after resorption of a pleural exudate and reactive fibrosis formation. It is most frequently seen in asbestos-related pleural disease, but is also seen in association with any (exudative) pleural effusion. A platelike atelectasis (synonym: discoid atelectasis) is a linear or planar opacity representing a portion of the lung with decreased volume, usually seen in lower lung zones. Figure 2 Patient with pleural empyema (note pleural split sign and air inclusions after pleurodesis) with a compression atelectasis of the lung parenchyma. Clinical Presentation Physical changes and symptoms depend on the size of the atelectasis and on the underlying and accompanying respiratory diseases. In patients with right middle lobe atelectasis, the upper and lower lobe will fill the space occupied by the collapsed lung, and breath sounds can be 2. Figure 3 Patient with a central perihilar tumor and upper lobe atelectasis: the curvilinear delineation of the atelectasis of the upper lobe indicates a central tumor as underlying disease (Golden S-sign). In most cases the type of atelectasis and the underlying disease can also be determined. Imaging the collapse of one or multiple complete lung lobes causes distinct imaging features based on the volume loss on one side, the displacement of fissures and elevation of the ipsilateral diaphragm (juxtaphrenic peak), the mediastinal and hilar structures, and the compensatory overinflation of the remaining lung. This represents a valuable finding for differentiating atelectasis from a tumor or pneumonia, both showing a less intense and more inhomogeneous enhancement. A rounded atelectasis describes a peripherally located, rounded or wedge-shaped atelectasis (sometimes mimicking a bronchogenic neoplasm) that is always adjacent to pleural thickening. Eur Radiol 23:9 Stark P, Leung A (1996) Effects of lobar atelectasis on the distribution of pleural effusion and pneumothorax. J Thorac Imaging 11:145 Ashizawa K, Hayashi K, Aso N et al (2001) Lobar atelectasis: diagnostic pitfalls on chest radiography. It is an important cause of end-stage renal failure, a consequence of the association of multiple Autoimmune Pancreatitis 107 factors, including decreased renal blood flow, intrarenal atherosclerotic arterial disease, atheroembolism, diabetes, increased oxidative stress, medullary hypoxia, endothelial dysfunction, and inflammation. Hypertension, Renal Autogenous Dialysis Fistula A A surgically created, direct communication in between an artery and a corresponding superficial vein allowing increased blood flow through the vein in order to provide luminal dilatation and thickening of the vein wall. Fistula, Hemodialysis Athyroid the physiological manifestation where there is a complete absence of thyroid function or hormone production. The histologic and clinical features are virtually indistinguishable from chronic viral hepatitis.
Cheap malegra fxt 140mg with amex. 10 Natural Home Remedies For Erectile Dysfunction Impotency Premature Ejaculation (+18).
Syndromes
- Forgotten tampon or foreign body
- Decide on the best treatment for the most common type of kidney stone, which is made of calcium. This type of stone may occur when the kidney leaks too much calcium into the urine.
- What drugs, vitamins, herbs, and other supplements you are taking, even ones you bought without a prescription
- Problems with the position and shape of the large arteries
- Nausea
- The kidneys begin to leak and protein (albumin) passes into the urine.
- Marfan syndrome
- Brain aneurysms
- Warm up before exercising and cool down afterward.
- Have you had a fever higher than 100 degrees F?
May communicate with the intercostobrachial nerve erectile dysfunction pump for sale order malegra fxt 140 mg online, which arises as a lateral branch of the second intercostal nerve impotence fonctionnelle buy malegra fxt 140mg line. Runs between the axillary artery and vein and then runs medial to the brachial artery impotence causes and cures buy 140mg malegra fxt free shipping. Runs behind the axillary artery and accompanies the thoracodorsal artery to enter the latissimus dorsi muscle erectile dysfunction protocol jason trusted 140 mg malegra fxt. It results in loss in function of the extensors of the arm, forearm, and hand and produces a wrist drop. Innervates the deltoid and teres minor muscles and gives rise to the lateral brachial cutaneous nerve. Passes posteriorly through the quadrangular space accompanied by the posterior circumflex humeral artery and winds around the surgical neck of the humerus (may be injured when this part of the bone is fractured). It results in weakness of lateral rotation and abduction of the arm (the supraspinatus can abduct the arm but not to a horizontal level). Injury to the radial nerve is caused by a fracture of the midshaft of the humerus. It results in loss of function in the extensors of the forearm, hand, metacarpals, and phalanges. It also results in loss of wrist extension, leading to wrist drop, and produces a weakness of abduction and adduction of the hand. Innervates all of the flexor muscles in the anterior compartment of the arm, such as the coracobrachialis, biceps, and brachialis muscles. Injury to the musculocutaneous nerve results in weakness of supination (biceps) and flexion (biceps and brachialis) of forearm and loss of sensation on the lateral side of forearm. Passes through the cubital fossa, deep to the bicipital aponeurosis and medial to the brachial artery. Enters the forearm between the humeral and ulnar heads of the pronator teres muscle, passes between the flexor digitorum superficialis and the flexor digitorum profundus muscles, and then becomes superficial by passing between the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor carpi radialis near the wrist. In the cubital fossa, it gives rise to the anterior interosseous nerve, which descends on the interosseous membrane between the flexor digitorum profundus and the flexor pollicis longus; passes behind the pronator quadratus, supplying these three muscles; and then ends in sensory "twigs" to the wrist joint. Innervates all of the anterior muscles of the forearm except the flexor carpi ulnaris and the ulnar half of the flexor digitorum profundus. Enters the palm of the hand through the carpal tunnel deep to the flexor retinaculum; gives off a muscular branch (recurrent branch) to the thenar muscles; and terminates by dividing into three common palmar digital nerves, which then divide into the palmar digital branches. Innervates also the lateral two lumbricals, the skin of the lateral side of the palm, and the palmar side of the lateral three and one-half fingers and the dorsal side of the index finger, middle finger, and one-half of the ring finger. Injury to the median nerve may be caused by a supracondylar fracture of the humerus or a compression in the carpal tunnel. It results in loss of pronation, opposition of the thumb, and flexion of the lateral two interphalangeal joints and impairment of the medial two interphalangeal joints. It also produces a characteristic flattening of the thenar eminence, often referred to as the ape hand. Descends posteriorly between the long and medial heads of the triceps, after which it passes inferolaterally with the profunda brachii artery in the spiral (radial) groove on the back of the humerus between the medial and lateral heads of the triceps. Pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to enter the anterior compartment and descends anterior to the lateral epicondyle between the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles to enter the cubital fossa, where it divides into superficial and deep branches. Gives rise to muscular branches (which supply the brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus), articular branches, and posterior brachial and posterior antebrachial cutaneous branches.