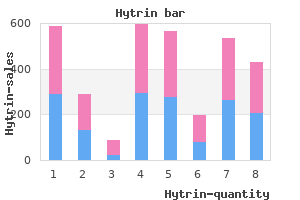
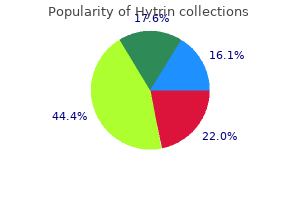
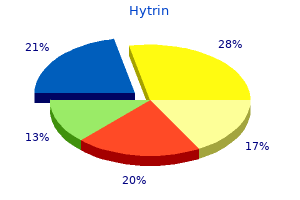
"Hytrin 5mg visa, arrhythmia burlington ma".
By: Z. Stejnar, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Co-Director, Larkin College of Osteopathic Medicine
This technique offers clarity and discussion pulse pressure 2012 order hytrin with amex, while supporting the establishment of realistic action plans blood pressure medication lip proven hytrin 1 mg. Review of the plan at intervals assists the patient and the educator in evaluating progress towards the goal prehypertension third trimester buy generic hytrin 2 mg online, if the goal is appropriate or if expectations and action steps need to be altered arteria hepatica communis purchase 2mg hytrin. In addition, it has also evaluated progress, and has provided tools for data documentation, tabulation, configuration, aggregation, analysis and review. Educators are encouraged to consider offering more time to identifying these problemsolving goals. Of note, patients seldom identified more than one goal, and clearly not more than one of substance, yet, as was referenced, the domains of healthy coping and problem-solving may be more useful in the long-term behavior changes that help patients toward successful accomplishments, rather than just the familiar food, activity, monitoring references [68]. In summary, educators should utilize of a wide variety of models and techniques that enhance the acquisition of information, and offer an interesting and creative educational, learning and empowering environment for all the learners, educators and patients alike. Maintaining and promoting achievement Measurable behavior change is the unique outcome of working with a diabetes educator. Healthy People 2010 has identified the need to increase the percentage of patients with diabetes receiving education, so that the current 40% would be increased to be at least 60% [68]. The structure helps to assess current preferences and behaviors of the individual with diabetes, discuss potential benefits, barriers, problem-solving and set a mutually agreed upon plan of behavioral interventions. Methods for setting up measurable indicators, monitoring schedules and documentation are needed for evaluation. Summary information is then available for the patient, health care team, and potentially for insurance and regulatory purposes. The effectiveness of disease and case management for people with diabetes: a systematic review. Metaanalysis of randomized educational and behavioral interventions in type 2 diabetes. Self-management aspects of the improving chronic illness care breakthrough series: design and implementation with diabetes and heart failure teams. Effects of self-management training in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, prospective trial. Behavior change and diabetes education have been shown to be effective for short-term outcomes [71,72]. Clinician and educator time will be well spent by individualizing care plans, paying attention to the process of educational information delivery methods and offering patient-centered care. Effectiveness of self-management training in type 2 diabetes: systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Translating the chronic care model into community: results from a randomized controlled trial of a multifaceted diabetes care intervention. National Standards for diabetes self-management education: what do they mean for providers? Motivational interviewing and diabetes: what is it, how is it used, and does it work? Psychosocial predictors of relapse among diabetes patients: a 2-year follow-up after inpatient diabetes education. A 5-year randomized controlled study of learning, problem solving ability, and quality of life modifications in people with type 2 diabetes managed by group care. Patient perceptions of quality of life with diabetes-related complications and treatments. Does patient perception of consultation concord with professional perception of consultation. American Diabetes Association and Healthy Interactions announce a collaboration to transform diabetes education. Group based training for self-management strategies in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Review: group based education in selfmanagement strategies improves outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Experience-based group education in type 2 diabetes a randomised controlled trial. The clinical effectiveness and cost effectiveness of patient education models for diabetes (April 2003). How to Assess Structured Diabetes Education: An improvement toolkit for commissioners and local diabetes communities.
Diseases
- Sacral plexopathy
- Short stature talipes natal teeth
- Nephrosclerosis
- Pseudohermaphroditism mental retardation
- Cartwright Nelson Fryns syndrome
- Diaphragmatic hernia exomphalos corpus callosum agenesis
- Polydactyly postaxial
- Al Gazali Hirschsprung syndrome
- Mild cognitive impairment
- Chordoma
It is imperative that practical methods are applied to preserve and protect the milk during transport and storage can prehypertension kill you hytrin 1 mg with amex. The challenge facing policy makers is to balance the objectives of consumer protection hypertension 12080 order hytrin online from canada, safe food and livelihood security pre hypertension natural cure 5mg hytrin amex. This requires evidence-based methods that assess the risks posed by dairy products originating in the informal sector and determining how to manage these risks in ways that consider both health and economic protection of the poorer farmers and traders who constitute the majority of the dairy sector (Grace et al heart attack but i cover up buy generic hytrin 1mg on-line. Regulations, management strategies and control measures need to be appropriate with the end objective of ensuring the safety of the product and consumer health protection. Responsible authorities must have a policy and legislative framework for food safety and quality, adequate infrastructure and properly trained inspectors and personnel in place if they are to function effectively. This should provide a coordinated and a preventive approach to foodsafety management along milk and dairy-product chains. Food-safety decisions and policies should be based on an understanding of the priority risks associated with milk and dairy products in the national milk and dairy sector. Working with dairy farmers and milk and dairy processors is essential to identify appropriate control measures and ensure their application at the most effective part of the chain. Different countries, different dairy products and different production environments give rise to a range of diverse situations. Chapter 6 Safety and quality 261 A range of government controls can be applied to prohibit a certain practice or use of a substance or regulations can be put in place that set maximum levels for specific substances. Achieving a safe final product from raw milk to the point of consumption will require a combination of control measures that together should achieve the appropriate level of health protection. Preventive and control measures will not necessarily be the same in all countries or production environments they need to be appropriate to the level of assessed risk, local production and processing procedures and the differing characteristics of milk from various milking animals. For example, many countries rely on controls other than an organized heat-treatment step such as pasteurization: in East Africa, for example, milk produced by the smallholder sector and sold through informal channels is generally boiled by the consumer before drinking. This is effective for killing most pathogens; however, if the consumer is unaware of the potential dangers of unpasteurized milk or forgets or chooses not to boil the milk they may face higher risk of food-borne illnesses. Other control measures can also be put in place, including a shorter chain from producer to final consumer or the practice of the consumer purchasing smaller quantities as and when needed (Grace et al. Farm practices should ensure that milk is produced by healthy animals under acceptable conditions for the animals and in balance with the local environment. It is important that control measures are applied during both primary production and processing to minimize or prevent the microbiological, chemical or physical contamination of milk. A general distinction can be drawn between the types of control measures used for microbiological hazards and those used for chemical and physical hazards. In addressing microbiological hazards it is essential to prevent unhygienic practices and conditions in the production, processing and handling of milk and milk products. Minimizing the initial microbial load in milk and prevention of the growth of micro-organisms are key to ensuring the safety of milk and dairy products. Some issues that may influence the microbiological load include herd size, distance from collection centre to dairy, temperature of the milk when it reaches the dairy plant or market, presence or absence of a cold chain, and duration of transportation. Although pasteurization may reduce numbers of micro-organisms in milk, it is not a substitute for good hygiene practices, especially as milk may be consumed raw. On occasion pasteurization may not destroy all pathogens in the milk, especially if it is not done properly. To be effective, pasteurization does require a cold chain from the time the product is pasteurized until it is consumed. Furthermore, where pathogens enter dairy plants in contaminated raw milk the pathogens can persist in the plant in biofilms and contaminate subsequent batches of 262 Milk and dairy products in human nutrition bOx 6. However these methods are not always possible in all countries and alternative methods are needed that are safe, cheap and easily applicable under farm conditions. The effectiveness depends on the initial amount and type of microbiological contamination and the temperature during the treatment period. Pathogens such as Listeria monocytogenes in particular can survive and thrive in processing environments and contaminate milk and dairy products during or after processing. The control measures used for chemical and physical hazards in food are generally preventive in nature and focus on avoiding and minimizing their presence rather than elimination at a later stage. In addressing chemical hazards, attention should be given to maintaining a clean production environment and safe feed and water to reduce the potential introduction of chemical contaminants such as dioxins, heavy metals and mycotoxins, as well as implementation of good animal husbandry and practices to ensure that veterinary drugs, pesticides etc.
As is the case for schizophrenia arteria jugular hytrin 1mg low cost, there is growing evidence that patients with bipolar illness also have increased all-cause mortality blood pressure keeps rising best purchase hytrin, and evidence of increased cardiovascular disease hypertension 3rd class medical hytrin 5mg low price, when compared with the general population hypertension complications 1mg hytrin with visa. Again the findings of longitudinal studies in the face of confounders such as lifestyle differences and the effects of treatments can be difficult to interpret. It is likely that those patients with bipolar illness who are exposed to long-term use of antipsychotic drugs (the majority) will have similar outcomes to those of patients with schizophrenia. Other drugs used in bipolar patients such as lithium and sodium valproate are also associated with weight gain, but there has been much less research on their wider metabolic effects to date. Case history 2: the interaction of schizophrenia and diabetes Timothy is a 30-year-old man who was admitted to a hospital with an acute psychotic illness. Following a diagnosis of schizophrenia, he was treated with an atypical antipsychotic and after this remained well both physically and mentally. His psychiatrist was concerned that the antipsychotic may have been involved in the development of his diabetes and switched him to an alternative antipsychotic. His diabetes did not resolve and proved more difficult to control until the original medication was restarted and his mental state improved. A particular difficulty in establishing whether schizophrenia and its treatment increase the risks of diabetes results from the fact that important known risk factors differ between populations, leading to a high degree of confounding in most epidemiologic studies. The risk factors with large effect sizes include: · Overweight and obesity; · Family history; · Age; and · Ethnicity. It is likely that the disease and its treatment have effects that are of smaller size than these, and so failure to match adequately for these confounders can easily yield results that are uninterpretable (Figure 55. Added to this is the fact that most studies are retrospective, and that patients tend to be exposed to a wide range of different antipsychotic drugs over the course of their illness. Prospective studies using single agents are much fewer in number, 946 Psychiatric Disorders and Diabetes Chapter 55 although reviews of such studies are now beginning to appear. Consequently, we are faced with many studies that give inconsistent and often contradictory results. In order to overcome some of these difficulties, studies in drug naпve, first-episode patients have been instructive in determining the possibility of an underlying abnormality in glucose metabolism associated with schizophrenia. In two small cross-sectional studies of first-episode drug naпve individuals in Ireland, 1015% of participants had impaired fasting glycemia and were more insulin resistant than healthy control subjects [36,37]. Firstepisode patients were also found to have significantly higher waist: hip ratios, and over three times as much visceral fat (a predictor of insulin resistance) when assessed by computed tomography scanning [38]. A study from India found that non-fasting blood glucose concentrations were higher in those with first-episode psychosis than healthy controls [39], while other studies have found differences in body composition between first-episode patients and healthy control subjects but without glucose changes [40]. The consensus that emerges from the current literature is that having schizophrenia is associated with a two- to fourfold increase in risk of developing diabetes, which leads to an overall prevalence of diabetes of 1015% in Western populations. Although subjected to much less systematic study to date, there is a suggestion in the literature that patients with bipolar disorder are also at increased risk of developing diabetes, with a relative risk estimated at two- to threefold. Similar caveats about the effects of treatments and lifestyle differences to those for schizophrenia apply. There are significant numbers of people with diabetes under the age of 40 years and therefore this issue should not be ignored even in those with a recent diagnosis of mental illness. Atypical vs atypical Atypical vs typical Any antipsychotic medication Schizophrenia Traditional risk factors. Association of diabetes mellitus with the use of atypical neuroleptics in the treatment of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159:561566 and National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey 20012002. Mechanisms of the association There are many difficulties in disentangling the possible mechanisms underlying the apparent associations between psychotic illness and diabetes. Diabetes, schizophrenia and bipolar illness all appear to be strongly heritable, and genetic associations appear to be likely (Figure 55. Shared susceptibility loci are now being investigated using linkage and candidate gene approaches [13]. Other factors that may underlie the association include a poorer diet, with lower intake of fruit and vegetables and much higher intake of fat, lower levels of physical activity, urbanization and higher rates of smoking among patients [44]. These findings have been documented consistently in several studies; however, it is difficult to assess the size of the effect that they may contribute to the observed association. The role of antipsychotic medication in contributing to the association remains under debate. There is reasonably strong evidence that most antipsychotic drugs are associated with an increase in risk of developing diabetes, but proof of causation has not been firmly established.
From within this neoliberal view blood pressure quick remedy 2mg hytrin with amex, Africa has to "catch up" to and "be taught" how to emulate and achieve the standards promulgated in mainstream media blood pressure 7850 buy 2 mg hytrin amex. Through the lens of an alternative realism blood pressure medication enalapril side effects buy hytrin 1 mg otc, however blood pressure ranges and pulse cheap 5mg hytrin otc, such narratives can be reshaped. The African philosophy of ubuntu is one example of a deeply relational ethic from within which development can be reconceptualized as "freedom" in terms of democratic ideals and which can be used as a guiding principle for media work and the refashioning of (reality television) images. Specifically, we use the historical research method to explore and explain the ideological discourses, polity contours and social forces that have overlain the role of radio as both an index and an instrument of development in Ghana. The evidence reveals that radio has transitioned through three key milestones in how the technology has been appropriated and applied to national development efforts: from transplantation, through transmission, to transaction. Each of these phases coincides, incidentally, with paradigm shifts in development communication theorizing: from modernization through diffusion to participation. They also coincide, broadly, with three distinctive epochs of ideological shifts in the historical accounting on radio for development in Ghana: from British imperial hegemony, through post-independence command-and-control, to contemporary liberal pluralism. Fьr die Lдnder des Globalen Sьdens - aber nicht nur fьr sie - steht dabei viel auf dem Spiel, einschlieЯlich der Gefahr eines neuen, digitalen Kolonialismus. Die Publikation untersucht, wo die Potenziale und Grenzen digitaler Lцsungsansдtze liegen. Sie analysiert, was sich aus vermeintlichen Vorzeigeprojekten wie dem mobilen Bezahlsystem M-Pesa oder der Verbreitung des bargeldlosen Bezahlens in Indien lernen lдsst. Die Autoren untersuchen auch, ob die Digitalisierung transnationaler Lieferketten nicht nur die Transparenz erhцht, sondern auch die Wertschцpfung bei den Arbeiterinnen und Arbeitern auf den Kaffee- und Sojaplantagen oder in Fabriken. Fьr eine faire Gestaltung der Digitalisierung mьssen vor allem folgende Fragen beachtet werden: Wie kцnnen benachteilige Bevцlkerungsgruppen in den lдndlichen Regionen Afrikas oder Bewohnerinnen und Bewohner von Armenvierteln in den Megacities einen besseren Zugang zu Arbeit und Grunddienstleistungen erhalten? Welcher MaЯnahmen bedarf es, um fьr Menschen in Asien und Lateinamerika die Risiken des digitalen Wandels zu minimieren und dessen Potenziale zu erweitern? Die Studie schlieЯt deswegen mit neun Bausteinen zum Aufbau einer fairen Digitalisierung. It includes 40 country reports from countries as diverse as Benin, Argentina, India, Russia and Ukraine, as well as three regional reports. Making Sense of Digital Disintermediation and Development: the Case of the Mombasa Tea Auction / Christopher Poster, Mark Graham, and Timothy Mwolo Waema -Development or Divide? Problematizing the Discourse on Connectivity in Logistics and Communication / Stefan Ouma, Julian Stenmanns, and Julia Verne. After immersing herself in factory towns, slums, townships, and favelas, Payal Arora assesses real patterns of internet usage in India, China, South Africa, Brazil, and the Middle East. She finds Himalayan teens growing closer by sharing a single computer with common passwords and profiles. Why do citizens of states with strict surveillance policies appear to care so little about their digital privacy? What drives young Indians to friend "foreign" strangers on Facebook and give "missed calls" to people? Through extensive fieldwork, Arora demonstrates that the global poor are far from virtuous utilitarians who mainly go online to study, find jobs, and obtain health information. She reveals habits of use bound to intrigue everyone from casual internet users to developers of global digital platforms to organizations seeking to reach the next billion internet users. Sustainable digitalization: guidelines for a digitalization we need for the future we want. Without proper discussions on benefits or risk, without democratic control and regulations, technologies have the potential to lead to more and new social, economic and ecological problems. Important first steps have been made to discuss the role of technology and the digital world. Yet we have to continue to actively shape the path of a truly sustainable digitalization. Michel Bauwens, Vasilis Kostakis, Alex Pazaitis: Peer to peer: the commons manifesto.
Hytrin 5 mg line. UA 704.