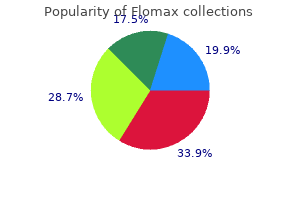
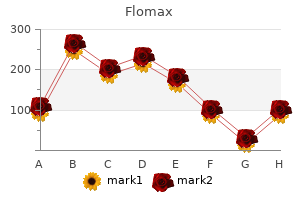
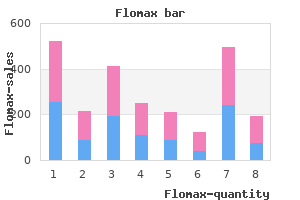
"Flomax 0.2 mg with visa, prostate 59".
By: P. Rune, M.A., M.D.
Program Director, New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University
Comparison of treatment strategies in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial prostate exam purchase flomax 0.4 mg line. A randomized prostate cancer 2b purchase cheap flomax online, double-blinded mens health yoga poses cheap flomax line, placebo-controlled pilot study of probiotics in active rheumatoid arthritis mens health testosterone buy cheap flomax line. Bacterial overgrowth during treatment with omeprazole compared with cimetidine: a prospective randomised double blind study. Mackay1 1 Department of Immunology, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia. Summary: Certain autoimmune diseases as well as asthma have increased in recent decades, particularly in developed countries. This may be particularly relevant to human inflammatory diseases, several of which associate with western lifestyle and obesity. While several studies and reviews (including by us) have highlighted the direct effects of dietary molecules on immune cells (4, 5), a new and possibly equally important element is the gut epithelium. The gut is lined by epithelial cells, which provide an important physical barrier and defense against pathogens. These included autoimmune disorders such as Type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis. This chapter suggests that a series of environmental factors, most of them microbial, have led to a decrease in the efficiency of our immunoregulatory mechanisms because we are in a state of evolved dependence on organisms with which we co-evolved (and that had to be tolerated) as inducers of immunoregulatory circuits. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol (2012) 42:5-15 and tarmac" urbanization in the early nineteenth century there has been a progressive increase in immunoregulatory problems attributable to depletion from the urban environment of organisms with which mammals co-evolved, and that had been tasked by co-evolutionary forces with a crucial role in setting up "normal" background levels of immunoregulation (this will be explained, expanded and referenced below). On the other hand, the recent nature of these increases makes it certain that the major underlying cause is environmental. The role of genetic factors cannot be more than to determine which individuals develop the disease after the environmental changes have occurred. Figure 1 lists some relevant factors, and also emphasizes the immunoregulatory role of the gut. One of the most important discoveries in recent years is the fact that manipulations of the immune system (or loss of the Old Friends! However, this did not mean that MyD88 was directly involved in the autoimmune response to cells in the pancreas. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol (2012) 42:71-78 Abstract Autoimmune diseases are characterized by tissue damage and loss of function due to an immune response that is directed against specific organs. When the zonulin pathway is deregulated in genetically susceptible individuals, autoimmune disorders can occur. Zonulin Introduction the intestinal epithelium is the largest mucosal surface providing an interface between the external environment and the mammalian host. Also pivotal is the regulation of molecular trafficking between the intestinal lumen and the submucosa via the paracellular space. The connection between infection and autoimmune disease is often explained by a mechanism known as "molecular mimicry," whereby microbial antigens are postulated to resemble self-antigens [1]. Microbial influences on epithelial integrity and immune function as a basis for inflammatory diseases. To understand immune-mediated pathways involved in the regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. It acts as a selectively permeable barrier, permitting the absorption of nutrients, electrolytes, and water while maintaining an effective defense against intraluminal toxins, antigens, and enteric flora. The protein networks connecting epithelial cells form 3 adhesive complexes: desmosomes, adherens junctions, and tight junctions. Over the past decade, there has been increasing recognition of an association between disrupted intestinal barrier function and the development of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. In this review we summarize the evolving understanding of the molecular composition and regulation of intestinal barrier function. We discuss the interactions between innate and adaptive immunity and intestinal epithelial barrier function, as well as the effect of exogenous factors on intestinal barrier function.
Syndromes
- Other cardiac disorders that weaken the heart
- Delayed growth and development (failure to thrive in infancy)
- Diabetes
- Some bleaches
- Intimacy and sexuality
- The time it was swallowed or contacted
- Heart failure
Thus prostate procedures generic 0.2mg flomax, transient bacteremia can cause a large number of organisms to be delivered to this region prostate cancer 83 year old man cheap flomax online master card. Bacteria normally cleared by synovial macrophages can be overwhelmed when presented with a large quantity of organisms prostate 049 discount flomax 0.4mg fast delivery. Proteolytic enzymes produced by bacteria and inflammatory cytokines incite damage to the articular cartilage prostate 3 times normal size buy flomax line. This process begins early in the infection, and its effects may render the articular surface susceptible to future degenerative joint disease. Furthermore, swelling of the joint capsule may predispose the femoral head to avascular necrosis due to ischemia of the capital femoral epiphysis. Dislocation or subluxation can also result from the increased intracapsular pressure (2). An important concept to emphasize is that the inflammatory process and tissue damage may progress despite the fact that the causative organisms have been eradicated. Children with septic arthritis all present with one common feature, pain to the affected limb. Joint pain may present as refusal to walk, to bear weight, or to utilize the affected limb. Often the children have fever and they can appear toxic to well appearing in their presentation. A history of trauma or upper respiratory infection in the weeks prior is sometimes elicited, which may mislead one from the true diagnosis of septic arthritis. Furthermore, septic arthritis may be a complication for patients with a history of recent surgery, urinary tract infection, and infection due to varicella zoster virus (due to secondary cutaneous infection of the lesions with Staph aureus or group A strep) (1). On physical exam, swelling, tenderness, erythema, and warmth may be apparent to joints with little overlying tissue. However in a deep (well enclosed) joint such as the hip, these findings may be minimal to absent. Subtle findings such as a loss of natural body curvatures or normal skin creases may be all that is present. Thus, examination of the opposite side for symmetry is an important aspect of the physical exam. Range of motion is the most sensitive method to determine the presence of joint effusion (2). Children with septic arthritis often have significantly decreased and painful range of motion since any movement that stretches the joint capsule produces severe discomfort. In infants with septic arthritis of the hip, the classic physical finding is of a child lying motionless with his/her leg externally rotated and abducted. In septic arthritis of the axial skeleton and pelvis, direct compression of the joints may be the only way to produce clinical signs. It is important to examine all the joints of the lower extremities in a child with a limp, because the child may complain of knee pain, when in fact it is the hip that is affected. Examination for signs of meningitis and performing a lumbar puncture when indicated is important in children who are susceptible to Haemophilus influenza, type B (but one would not necessarily know this until gram stain and/or culture information is available). One study found that 30% of children with septic arthritis due to this organism had concurrent meningitis (2). Haemophilus influenzae, type B (HiB) infections are currently almost nonexistent because of widespread effective HiB immunization. In the neonatal period septic arthritis often is present concurrently with acute osteomyelitis of the adjacent bone. The differential diagnosis of a child with fever and joint pain includes: septic arthritis, transient synovitis, reactive arthritis, trauma, acute rheumatic fever, Henoch-Schonlein purpura, Kawasaki disease, serum sickness, lyme disease arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, hematologic cancer, and connective tissue disease (i. Toxic synovitis (also known as transient synovitis) of the hip is a viral or post infectious process causing acute arthritis that is important because it often causes a diagnostic dilemma for the clinician. Transient synovitis of the hip is often preceded by an upper respiratory tract infection or pharyngitis in previously healthy children. The etiology is unclear; however children with this condition may have a predisposition for hypersensitivity reactions. Rarely is joint aspiration performed, despite the Page - 622 presence of a hip effusion if the clinical findings and laboratory studies are suggestive of this diagnosis. Toxic synovitis is a diagnosis of exclusion, and treatment consists of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications and bed rest. Overall prognosis is usually good (about 70% of patients have resolution of their symptoms within two weeks) (3), but avascular necrosis may occur in some patients.
Nephrotoxicity of iso-osmolar iodixanol compared with nonionic low osmolar contrast media: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials prostate lower back pain buy 0.4 mg flomax amex. There is only moderate quality of evidence and overall prostate cancer gleason score 9 cheap flomax 0.4mg online, no benefit-or mens health 9 minute kettlebell workout 0.4mg flomax with visa, at least prostate 40 gpa scale buy cheap flomax 0.2mg line, no consistent benefit-was found of nonionic isoosmolar (iodixanol) contrast media compared to lowosmolar ionic or nonionic contrast media. The volume of contrast medium, volume of saline administered, frequency of coronary interventional procedures, and severity of baseline kidney disease and of diabetes mellitus were similar between treatments. Finally, a recent meta-analysis457 (Figure 14) analyzed studies comparing iodixanol with low-osmolar contrast media. In the studies that included only patients with decreased kidney function after i. The clinical heterogeneity between all these studies, as far as basal kidney function and prevalence of diabetes mellitus are concerned, hampers the ability to compare the results across studies, but can widen the applicability of consistent findings across different risk groups provided the mechanisms of contrast-induced nephrotoxicity are the same. Finally, different types and amounts of volume expansion and different pharmacological preventive strategies have been used throughout the studies, making conclusive comparisons virtually impossible. Although overall the number of patients is substantial, there is heterogeneity among the comparators with which iodixanol has been compared. In addition, the cost of iodixanol is probably higher than the cost of most of the low-osmolar contrast agents. Based on evidence profiles (Suppl Tables 19 and 20) and the most recent meta-analysis457 (Figure 14) of the studies comparing i. It is, however, difficult to determine whether this is simply due to spurious findings in a smaller number of comparisons, or due to true differences between low-osmolar agents. Until better head-to-head comparative studies among the different contrast media agents are available, the Work Group is unable to draw definite conclusions on the selection of iso-osmolar vs. This conclusion is supported by the above-mentioned recent meta-analysis457 which, in seven studies comparing i. In head-to-head comparisons with different low-osmolar agents, iodixanol has been shown to be superior to Additional studies with head-to-head comparisons among the different contrast media should be performed in order to draw definite conclusions on the selection of iso-osmolar vs. Neurohumoral effects of volume expansion that may attenuate radiocontrast-induced medullary hypoxia include suppression of vasopressin as well as inhibition of the reninangiotensin axis; but an increased synthesis of vasodilatory renal prostaglandins may also play a role. Likewise, an effect of radiocontrast media to increase tubular fluid viscosity may be diminished by intravascular volume expansion. The sustained administration of isotonic saline before and after radiocontrast injection seems, thus, to be more protective than equivalent volumes of hypotonic saline. Systematic review: sodium bicarbonate treatment regimens for the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy. Meta-regression showed that small, poor-quality studies that assessed outcomes soon after contrast-media administration were more likely to suggest the benefit of bicarbonate (Po0. No clear effects of treatment on the risk for dialysis, heart failure, and total mortality were identified. In all studies, a minimum of 50 patients in both arms and publication as full paper were required for inclusion in the tables. Two patients in the normal saline group and none in the bicarbonate group needed dialysis. Based on this last prospective study, bicarbonate does not seem to be more efficient than saline. In addition, isotonic bicarbonate solutions are usually composed by adding 154 ml of 8. Since this mixing of the solution is often done at the bedside or in the hospital pharmacy, there is the possibility for errors leading to the infusion of a hypertonic bicarbonate solution. The potential for harm from dosing errors, and the added burden from preparation of the bicarbonate solution, has to be taken into account in clinical practice when making a choice between using bicarbonate rather than standard isotonic saline solutions.
Let arms hang in front of the thighs prostate cancer radiation oncology generic flomax 0.2 mg overnight delivery, and pull shoulder blades back and down Position feet hip-width apart with toes pointed straight ahead Slightly flex knees and engage the core to stabilize the body and prevent arching of the back (avoid rocking back and forth to complete the lift) Figure 4-18 prostate keep healthy buy flomax 0.4mg mastercard. Maintain a constant body position and raise dumbbells directly to the front until they are at shoulder level (Figure 4-18) 2 prostate cancer 5k san antonio buy 0.2mg flomax amex. Keep palms facing the ground and lower dumbbells slowly prostate cancer 2 causes flomax 0.2 mg discount, back to the start position Figure 4-20. Let arms hang to the sides to the thighs, and pull shoulder blades back and down Position feet hip-width apart with toes pointed straight ahead Slightly flex knees and engage the core to stabilize the body and prevent arching of the back (avoid rocking back and forth to complete the lift) Procedure 1. Maintain a constant body position and raise dumbbells to the sides until they are at shoulder level (Figure 4-19) 2. Keep palms facing the ground and lower dumbbells slowly, back to the start position Basics of Strength and Conditioning 41 Procedure 1. Barbell Standing Behind the Neck Shoulder Press Exercise Objective: Develop strength in the muscles of the shoulder girdle and teach the athlete to use the whole body to stabilize overhead loads Start Position 1. Barbell Push Press Exercise Objective: Develop explosive power in the hips and legs, as well as strengthen the shoulder muscles while stabilizing overhead loads Start Position 1. Place hands evenly on the bar, slightly wider than shoulderwidth, with a pronated grip Position bar behind neck and comfortably across the shoulders with shoulder blades pulled together, elbows pointed down with hands directly above them (Figure 4-23) Stand erect and take one or two steps back to position body in the center of the rack Place feet hip-width apart, toes pointed straight ahead, and slightly flex hips and knees with the weight centered on the feet (Figure 4-23) Head remains in a neutral position looking forward Engage the core to stabilize the body and prevent arching the back 4. From the start position, press the bar straight overhead by extending the arms and keeping the body stable (Figure 4-22) 2. At the top of the lift, the bar should be slightly behind the ears with elbows completely extended and in line with the shoulders, hips, and heels Lower the bar to its starting position across the shoulders in a controlled manner 4. Barbell Push Jerk Exercise Objective: Develop explosive power in the hips and legs, as well as strengthen the shoulder muscles while stabilizing overhead loads Start Position 1. Place hands evenly on the bar, slightly wider than shoulderwidth, with a pronated grip Position bar behind neck and comfortably across the shoulders with shoulder blades pulled together, elbows pointed down with hands directly above them (Figure 4-26) Stand erect and take one or two steps back to position body in the center of the rack Place feet hip-width apart, toes pointed straight ahead, and slightly flex hips and knees with the weight centered on the feet (Figure 4-26) Head remains in a neutral position looking forward Engage the core to stabilize the body and prevent arching the back Procedure 1. Lower into a quarter squat position by pushing hips back, flexing knees, letting the torso come forward, and transfer the weight onto the heels (Figure 4-24) Explosively extend hips and knees to accelerate the bar upward Drive the bar upward by extending arms completely, pressing it overhead At the top of the lift, the bar should be slightly behind the ears with elbows completely extended and in line with the shoulders and hips (Figure 4-25) As the bar is caught overhead, flex hips backward, keep knees behind toes, and sit into a quarter squat position Extend hips and knees to stand erect Lower the bar to the start position in a controlled manner 3. Lower into a quarter squat position by pushing hips back, flexing knees, letting the torso come forward, and transfer the weight onto the heels (Figure 4-27) Explosively extend hips and knees and go onto the balls of the feet to accelerate the bar upward Drive the bar upward with the shoulders and arms, and push the body under the bar (Figure 4-28) In the catch position, the bar should be slightly behind the ears with elbows completely extended and in line with the shoulders and hips Stabilize the body and step feet together so they are shoulder-width apart (Figure 4-29) Lower the bar to the start position in a controlled manner 3. From the start position, pull entire body up by squeezing the shoulder blades back and down, and flexing elbows 2. Standing Low Row Exercise Objective: Develop the muscles of the upper back as well as the stabilizers of the legs and core Start Position 1. Keep chest up, back flat, and core engaged, and take a few steps back to center your body in the machine Place feet hip-width apart, toes pointed straight ahead, hips and knees slightly flexed, and center weight on the feet (Figure 4-32) Knees should be directly over ankles with a slight forward lean of the torso so the shoulders are directly over the knees Fully extend elbows (Figure 4-32) 4. Pull-Ups Exercise Objective: Develop strength in the muscles of the upper back, arms, and abdominals Start Position 1. Place hands evenly on a bar slightly wider than shoulderwidth with a pronated grip 2. Let body hang completely from the bar, with elbows and hips fully extended, knees slightly flexed, and ankles crossed (Figure 4-30) 4. Maintain the start position and squeeze shoulder blades back and down while flexing elbows 2. Continue to pull the handle until it touches the upper abdomen (Figure 4-33) Return the bar to the start position in a slow, controlled manner Procedure 1. Pull the bar down until it touches the top of the chest (Figure 4-35) Return the bar to the start position in a slow, controlled manner Figure 4-32.
Discount 0.4 mg flomax amex. Young Man Visits A Shine Clinic.