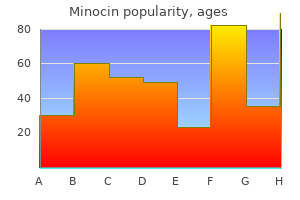
"Cheap minocin 50 mg without prescription, antibiotics dosage".
By: Z. Topork, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Assistant Professor, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Clinical manifestations antimicrobial bar soap cheap minocin line, risk factors bacteria necrotizing fasciitis discount minocin 50 mg on-line, and maternal and perinatal oucomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis bacteria habitat cheap minocin 50mg with visa. Embryology basal cells become high; the nuclei become elongated and the structure starts to grow downward into the dermis bacteria killing foods order minocin once a day. At the same time, mesenchymal cells and fibroblasts increase in number to form the rudiment of the hair papilla beneath the hair germ. These events are mediated by a second series of signals from the expanding epithelial cells. The outer cells of the hair peg are arranged radially to the long axis, and are columnar in shape, those at the advancing matrix end being conspicuously tall and narrow. As the germ develops, it grows obliquely downwards, and the advancing extremity becomes bulbous, gradually enveloping the mesodermal papilla. Proliferation and differentiation are then enhanced by a third series of signals emanating from the dermal papillae. At this bulbous hair-peg stage, two epithelial swellings appear on the posterior wall of the follicle. The lower one is the bulge to which the arrector muscle becomes attached, and the upper is the rudiment of the sebaceous gland. In many follicles, a third bud later appears above the sebaceous gland; this is the rudiment of the apocrine gland. Such rudiments develop in a large number of the follicles, including some on the scalp, face, chest, abdomen, back and legs, as well as in the axilla, mons pubis, external auditory meatus, eyelids, circumanal area, areola region of the breast, labia minora, prepuce and scrotum, where they survive in the adult. The matrix continues to burrow deeper, and above the root sheath the inner cells of the follicle grow upwards into the epidermis, to form the hair canal. There are also marked changes in certain cell adhesion proteins, notably E-cadherin and P-cadherin [15]. As the skin grows, these first germs become separated, and new rudiments develop between them when a critical distance, dependent on the region of the body, has been reached. Commonly, follicles occur in groups of three, with the hairs arranged on a straight, short line, more or less transverse to the grain or slant of the hair. There is no large-scale destruction of follicles during postnatal development, only a decrease in actual density as the body surface increases; nor do any new follicles develop in adult skin. Sebaceous glands [16,17] these are, at first, solid, hemispherical protuberances on the posterior surfaces of the hair pegs. At the end of fetal life, sebaceous glands are well developed and generally large. After birth, the size is rapidly reduced, and they enlarge to become functional again only after puberty. Eccrine glands [18,19] these start to develop on the palms and soles at about 3 months, but not over the rest of the body until the fifth month. In embryos of 12 weeks, the rudiments of eccrine sweat glands are first identifiable as regularly spaced undulations of the stratum germinativum. Cells that form the anlagen are oblong, palisading and lie closely together, but otherwise they do not differ from the rest of the stratum germinativum. In the overlying epidermis, columns of cells that are destined to form the intraepidermal sweat ducts are recognizable. Each column is composed of two distinct cylindrical layers, comprising two inner cells that are elongated and curved so that they embrace the inner cylinder. The intraepidermal duct appears to form by the coalescence of groups of intracytoplasmic cavities formed within two adjacent inner cells. In the intradermal segment, on the other hand, the lumen appears to form by dissolution of the desmosomal attachment plaques between the cells that compose the inner core of the eccrine duct germ. Dermis It was at one time believed that the mesenchymal cells forming the dermis came from the ventrolateral part of the somite, which for that reason was named the dermatome.
As such antibiotic 200 mg cheap minocin 50mg free shipping, amounts being attributed to principal investigators in connection with research can appear very high in total value transfer (especially across multiple companies) but be misleading about actual value received and provide no relevant information about influence antibiotics for acne flucloxacillin purchase minocin once a day. This disconnect is especially egregious in the oncology research space antibiotic mouthwash prescription minocin 50mg with mastercard, where patient care antibiotics for acute sinus infection buy generic minocin line, concomitant therapies, required diagnostic equipment, etc. Others may go further to attribute funds to site principal investigators, while others may go still further to attribute funds to all physicians (including sub-investigators) actually working with patients. However, without knowledge of the underlying assumptions made, third parties could reach different and sometimes incorrect conclusions. Context to the public about the potential differences in application and interpretation of Open Payments is still needed. Certain physicians, or their institutions, might react (or already have) by curtailing their ties to industry-sponsored research and development work, just when the pursuit of good science requires more partnership. This democratization of clinical trial design is likely to require an even greater absolute number of Oncology research and practice in the modern era require collaborations between academic physicians and industry. These collaborations provide challenges and opportunities that the entire oncology community must understand and address- especially the complexities that result from these relationships. These relationships which are necessary to continue advancing the field of oncology influence decisions from the level of the individual patient and provider, academic institutions, professional societies, and, most recently, national health policy. As we strive to provide the best and most promising therapies to our patients, we must acknowledge the issues surrounding relationships with industry and learn to navigate and overcome these challenges. Honoraria: Reshma Jagsi, International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. Ratain, Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Dicerna (Inst), OncoTherapy Science (Inst), PharmaMar (Inst). Scope and impact of financial conflicts of interest in biomedical research: a systematic review. Frequency, type, and monetary value of financial conflicts of interest in cancer clinical research. Association between pharmaceutical involvement and outcomes in breast cancer clinical trials. Disclosure of conflicts of interest by authors of clinical trials and editorials in oncology. Correlation between financial relationships with commercial interests and research prominence at an oncology meeting. Institutional academic industry relationship: results of interviews with university leaders. Financial conflict-of-interest policies in clinical research: Issues for clinical investigators. National evaluation of policies on individual financial conflicts of interest in Canadian academic health science centers. Health industry practices that create conflicts of interest: a policy proposal for academic medical centers. Attitudes toward research participation and investigator conflicts of interest among advanced cancer patients participating in early phase clinical trials. Televised medical talk shows-what they recommend and the evidence to support their recommendations: a prospective observational study. To ban or not to ban-that is the question: the constitutionality of a moratorium on consumer drug advertising. United States Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Guidance For Industry on Consumer-Directed Broadcast Advertisements; Availability. Innovation and Marketing in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Emerging Practices, Research, and Policies. The opinions and experiences of family physicians regarding direct-to-consumer advertising.
Therefore antibiotics empty stomach buy minocin 50mg amex, there is a need for predictive biomarkers that are selected on the basis of their capacity to classify patients according to the degree of benefit from treatment or the risk for significant toxicity antibiotics for uti treatment discount 50mg minocin fast delivery. Neoadjuvant studies that allow access to blood and tumor Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest Relationships are considered self-held and compensated unless otherwise noted antibiotics vs antibacterial minocin 50mg fast delivery. Tarhini antibiotic 7 days to die cheap minocin 50 mg with amex, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Morphotek, Novartis, Pfizer Oncology. Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. Prognostic factors in metastatic melanoma: a pooled analysis of Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trials. Local recurrence in malignant melanoma: long-term results of the multi-institutional randomized surgical trial. High- and low-dose interferon alfa-2b in high-risk melanoma: first analysis of intergroup trial E1690/S9111/C9190. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. Surgical resection with or without preoperative chemotherapy in oesophageal cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on local-regional disease in women with operable breast cancer: findings from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18. Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in lymph node melanoma metastases: a histopathologic prognostic indicator and an expression of local immune response. Immunotype and immunohistologic characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells are associated with clinical outcome in metastatic melanoma. Immune profile and mitotic index of metastatic melanoma lesions enhance clinical staging in predicting patient survival. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in metastatic malignant melanoma and response to interferon alpha treatment. Comparison of intramuscular and intravenous recombinant alpha-2 interferon in melanoma and other cancers. Immune monitoring of the circulation and the tumor microenvironment in patients with regionally advanced melanoma receiving neoadjuvant ipilimumab. Neoadjuvant ipilimumab in locally/regionally advanced melanoma: clinical outcome and immune monitoring. Immune related pathways/genes identified through tumor gene expression profiling can significantly predict neoadjuvant ipilimumab clinical benefit. Neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced melanoma: new strategies with targeted therapies. Neoadjuvant treatment with dabrafenib of unresectable localizations from occult melanoma. Interferon-beta therapy for malignant melanoma: the dose is crucial for inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis of melanoma cells. A phase 2 study of highdose allovectin-7 in patients with advanced metastatic melanoma. Ipilimumab plus sargramostim vs ipilimumab alone for treatment of metastatic melanoma: a randomized clinical trial. As these strategies are being tested in clinical trials, preclinical and early clinical trial data are now emerging about which combinatorial approaches might be best for these patients. Over the past decade, however, great advances in immune-targeted and molecular-targeted therapies have led to a therapeutic revolution.
Minocin 50mg with mastercard. Fighting Super Bugs: Overcoming Antibiotic Resistance.