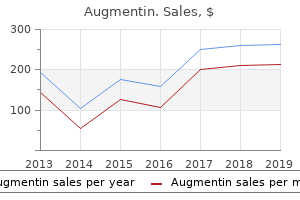
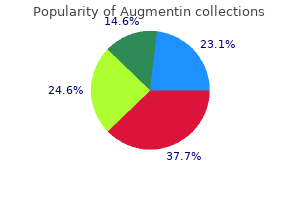
"Buy augmentin 375mg visa, bacteria you can eat".
By: F. Ningal, M.A., M.D.
Vice Chair, Georgetown University School of Medicine
Because alcohol dehydrogenase has a much higher affinity for ethanol than for either ethylene glycol or methanol antibiotics for uti online best purchase augmentin, the use of ethanol as a competitive inhibitor is the traditional treatment xiclav antibiotic purchase 375mg augmentin with mastercard. However antibiotic resistance japan augmentin 1000 mg with amex, in some patients with marked ethanol tolerance this rate will need to be doubled antibiotic resistance uk purchase cheap augmentin on-line. Fomepizole (4-methylpyrazole), a competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase, has replaced ethanol as the treatment of choice. An initial loading dose of 15 mg/kg body weight is followed 12 hours later by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for four doses, then 15 mg/kg every 12 hours for four more doses. Although fomepizole, because of its potency, has begun to call into question the need for dialysis, until more studies are available it is recommended that dialysis be instituted in all patients with suspected ingestions of ethylene glycol or methanol who have end-organ damage (kidney failure or visual impairment) and whose pH is less than 7. Hemodialysis can also help improve the acidosis by providing a source of bicarbonate. It is important to double the rate of any ethanol infusion or to increase the dose of fomepizole while the patient is receiving hemodialysis. For either ingestion, gastric lavage with charcoal should be performed when ingestion has occurred within the preceding 2 to 3 hours. Metabolic acidosis results from the accumulation of both lactic and ketoacids, whereas salicylic acid itself accounts for only a small quantity of the acid load. The patient may also complain of tinnitus when serum concentrations of salicylic acid reach 20 to 45 mg/dl or higher. Both noncardiogenic pulmonary edema and upper gastrointestinal bleeding may occur. In the setting of salicylate overdose, peak serum concentrations are achieved 4 to 6 hours after ingestion. The severity of the ingestion can be predicted by the Done nomogram, which plots the toxic salicylate level at varying points following ingestion. This nomogram cannot be used with chronic ingestions or with the ingestion of enteric-coated aspirin. In addition, because tissue salicylic acid is in equilibrium with the nondissociated compound in the plasma, alkalinization also decreases tissue levels. Concurrent alkalinization of the urine traps salicylate in the tubule, promoting its excretion. Hemodialysis is indicated in all patients with altered mental status, kidney failure that decreases renal excretion, volume overload that prevents the administration of bicarbonate, or salicylate levels greater than 100 mg/dl. This underreported acidosis occurs in patients who usually have underlying infections and are treated with acetaminophen even at therapeutic doses. Glutathione depletion decreases the negative feedback inhibition on -glutamylcysteine synthetase, resulting in an increase in pyroglutamic acid (5-oxoproline). The buffering of protons by bone results in the loss of calcium and negative calcium balance. In addition, chronic acidosis causes protein breakdown, muscle wasting, and negative nitrogen balance. It is rare for maintenance hemodialysis to be initiated solely for the purpose of correcting acidosis. The distal tubule defects can be further divided into those with hypokalemia and those with hyperkalemia. The precise cause of hyporeninemia has not been clearly defined, but the findings that hypertension is frequently present and that the disorder may be partly reversed with chronic furosemide use suggest that renin suppression may be secondary to chronic volume overload. Renin suppression alone should not cause hypoaldosteronism, because hyperkalemia is a potent stimulus of aldosterone secretion and anephric individuals still secrete aldosterone. The acidosis is primarily caused by decreased ammoniagenesis as a result of the associated hyperkalemia induced by the aldosterone deficiency. Hypoaldosteronism, by diminishing distal sodium reabsorption, also results in a less negative lumen potential, thus decreasing the rate of H+ secretion but not the electromotive force of the pump. However, when renal potassium handling is further perturbed by various stressors, marked hyperkalemia ensues with a decline in ammoniagenesis. These stressors include sodium depletion, which decreases delivery of sodium to the distal tubule; high potassium diet; and potassium-sparing diuretics or medications that further decrease renin and aldosterone levels, such as angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, or heparin.
They have a narrow zone of transition and are surrounded by areas of ill-defined sclerosis bacteria 2 in urine test discount augmentin 1000mg otc. The vertebral column retains a normal alignment and there is no loss of vertebral body height to suggest vertebral collapse infection game app buy augmentin 375 mg cheap. Within the limits of this single image antibiotic kill curve protocol order augmentin 1000 mg with mastercard, the cord appears capacious throughout antibiotic resistance recombinant dna discount augmentin 625 mg with amex, although review of the whole image series is recommended. Secondary bone deposits are approximately 100 times more common than primary bone tumours. This is most marked in the spine, where vertebral compression fractures can cause spinal canal stenosis from retropulsed bone fragments, which can encroach on the spinal cord causing compression and neurological compromise. Depending on cell type, tumour deposits upregulate either osteoclastic or osteoblastic activity, giving characteristic radiographic appearances. Those metastases with osteoclastic activity cause bone lysis, with soft tissue deposits destroying the adjacent bone and reducing the structural integrity. Osteoblastic metastases cause bone sclerosis, with new bone formation appearing as areas of increased density. The involved bones retain their normal morphology, but the heterotrophic bone has abnormal trabecular architecture, reducing the overall bone integrity. To confuse matters, some tumour types have metastases with both lytic and sclerotic components, and lytic bone metastases become sclerotic following treatment. A few metastases can also cause characteristic bone expansion and the common appearances are listed in Table 89. Bone scintigraphy, where radioactive phosphate particles are administered intravenously, is often appropriate in characterization of disease distribution and treatment response. It is highly sensitive with relatively low radiation exposure, and is useful to localize areas of possible disease for further assessment. There is also diffuse uptake of tracer noted in multiple ribs bilaterally as well as in multiple vertebrae at multiple levels. He complains of weight gain, tiredness and headache over the last few months with no resolution of symptoms despite diet and analgesia. Living at home with his wife and children, he has taken several sick days recently because of his symptoms. Examination Examination reveals a tired looking Caucasian man in no obvious discomfort. On neurological examination, visual field assessment reveals a bitemporal hemianopia. Within the suprasellar space there is a soft tissue mass measuring approximately 20Ч17mm which is well defined and isodense to the neighbouring brain tissue. The soft tissue mass demonstrates avid uniform enhancement centred on the pituitary fossa with suprasellar extension towards the optic chiasm and third ventricle. The sella is expanded as before but there is no obvious breach of the sella floor or extension into the sphenoid sinus. Within the limits of these images, the basal cisterns are preserved throughout and there is no evidence of hydrocephalus or tentorial herniation. Pituitary metastasis and lymphoma are very rare and would be an unlikely diagnosis considering there are no other systemic symptoms. Despite being benign, patients are frequently symptomatic depending on its size and functioning status. Patients with pituitary microadenomas (<10 mm) often present with symptoms of hormonal imbalance resulting from functionally active tumours, most commonly prolactin secreting with symptoms of amenorrhoea and infertility; instability of the adrenocortical, somatostatin and gonadotrophin axis can also occur. In this case, the patient has a pituitary macroadenoma (>10 mm) with symptoms resulting from mass effect related to tumour bulk. In addition, suprasellar tumour extension is causing compression of the optic chiasm and stretching of the prechiasmic optic nerve. With no intervention, the tumour will continue to grow and he will be at risk of visual loss, obstructive hydrocephalus and carotid artery involvement. This patient was referred to neurosurgery with successful tumour removal and complete symptom resolution. He is known to suffer from atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease and is currently being treated conservatively for claudication.
Buy generic augmentin 625 mg on-line. Antimicrobial resistance: a global health issue.
There is also evidence that the subunit can mediate basolateral extrusion of magnesium antibiotics given for tooth infection order augmentin 375mg mastercard. Mutation is associated with autosomal dominant inheritance of isolated hypomagnesemia antibiotics for uti types order augmentin 375mg amex, without other electrolyte disturbances bacterial tracheitis cheap augmentin 1000mg on-line. This paradox may relate to tissue-specific splice variants of the gene or differential interactions with tissue-specific Kv1 units bacteria breath test buy augmentin paypal. Electrolyte abnormalities cluster in this family with hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, suggesting a possible role for mitochondria in the metabolic syndrome. Its function is not yet known, but it may represent the postulated basolateral transporter mediating magnesium efflux, or a magnesium sensor. This autosomal dominant condition often manifests in children with severe hypertension and hypokalemic alkalosis. It resembles primary hyperaldosteronism, but serum aldosterone levels are quite low, and, for this reason, the disease also has been called pseudohyperaldosteronism. In their original description of the syndrome, Liddle and colleagues demonstrated that aldosterone excess was not responsible for this disease and that, although spironolactone had no effect on the hypertension, patients did respond well to triamterene or dietary sodium restriction. They proposed that the primary abnormality was excessive renal salt conservation and potassium secretion independent of mineralocorticoid. This hypothesis proved to be correct, and it is explained by excessive sodium channel activity. The autosomal recessive form is milder and resolves with time, but the autosomal dominant form is more severe and persistent. Type 2 disease differs from hypoaldosteronism in that it is a hypertensive condition. Type 2 pseudohypoaldosteronism is also known as Gordon syndrome or familial hyperkalemic hypertension. It is a mirror image of Gitelman syndrome, with hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, and hypercalciuria, although serum magnesium levels are normal. In a sense, this is a genetic analogue of the ingestion of black licorice, which contains glycyrrhizic acid that inhibits this enzyme. Inactivation of the enzyme results in failure to convert cortisol to cortisone locally in the collecting duct, allowing cortisol to activate mineralocorticoid receptors and produce a syndrome resembling primary hyperaldosteronism but, like Liddle syndrome, with low circulating levels of aldosterone. A gene on the X chromosome encodes the V2 receptor, and inactivating mutations in the V2 receptor gene cause the most common form of inherited nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Hou J, Renigunta A, Konrad M, et al: Claudin-16 and claudin-19 interact and form a cation-selective tight junction complex. Kleta R, Bockenhauer D: Bartter syndromes and other salt-losing tubulopathies, Nephron Physiol 104:73-80, 2006. Konrad M, Weber S: Recent advances in molecular genetics of hereditary magnesium-losing disorders, J Am Soc Nephrol 14:249-260, 2003. In Lifton R, Somlo S, Giebisch G, Seldin D, editors: Genetic diseases of the kidney, San Diego, 2008, Elsevier. The resultant chain of the hemoglobin molecule possesses a substitution of valine for glutamic acid at position 6, leading to an unstable form of hemoglobin (hemoglobin S). Under conditions of low oxygen tension, acidity, extreme temperatures, and other stressors, the altered hemoglobin undergoes polymerization, leading to "sickling" of red blood cells (Figure 40. These red cells are rigid, leading to both microvascular obstruction and activation of inflammation and coagulation. Worldwide, the prevalence of the hemoglobin S mutation varies greatly and is often highest in areas where malaria is endemic, related to the protection it affords against malarial infection. The renal medulla, with its lower oxygen tension, high osmolarity, lower pH, and relatively sluggish blood flow, is an ideal environment for "sickling" and microvascular obstruction. Similarly, co-inheritance of -thalassemia mutations reduces intracellular HbS concentration and leads to reduced hemolysis and fewer complications. Within the kidney, these pathologic mechanisms result in clinical manifestations that lead to changes in kidney hemodynamics, tubulointerstial damage, and in some patients, glomerular disease. Glomerulomegaly is evident even in patients without clinical disease and contributes to the hyperfiltration. Glomerular hyperfiltration likely is driven by vasodilatation of the afferent arteriole, which is thought to occur as a compensatory response to chronic tissue hypoxia. The exact mechanisms behind this response are not fully known, but it may be mediated by upregulation of prostaglandins and the nitric oxide systems.
Diagnosis Smears of clinical samples or cultures of sputum bacteria harmful discount augmentin 625 mg on-line, pus best antibiotic for sinus infection cephalexin order augmentin amex, or tissue are required for diagnosis virus jokes cheap 1000 mg augmentin with mastercard. Antigen detection in urine and serum may assist in diagnosing infection and in monitoring pts during therapy antibiotic quiz pharmacology 625mg augmentin. More indolent infections can be treated with itraconazole (200400 mg/d for 612 months). Among compliant immunocompetent pts, clinical and mycologic response rates are 9095%. Infection, which results from inoculation of the organism into the skin, is seen especially often in florists, gardeners, and nursery workers. Clinical Features · Plaque disease: Sporotrichosis is limited to the site of inoculation. Secondary lesions ascend along lymphatics draining the area, producing small painless nodules that erupt, drain, and ulcerate. For extracutaneous disease, itraconazole (200 mg bid) can be given, but AmB is more effective for life-threatening pulmonary disease or disseminated infection. Pulmonary infection follows inhalation of conidia and may disseminate to skin, lymph nodes, and adrenal glands. Clinical manifestations are similar to those of disseminated histoplasmosis, with fever, weight loss, generalized lymphadenopathy, and hepatomegaly. AmB is the treatment of choice for severely ill pts; less severe disease may be treated with itraconazole. The clinical presentation is generally nonspecific, with fever and skin lesions that become necrotic and resemble ecthyma gangrenosum. Blood cultures are positive in 50% of cases; in contrast, blood cultures are rarely positive in aspergillosis or zygomycosis. Fusarium species are often resistant to antifungal agents; high-dose AmB or voriconazole (6 mg/kg q12h for the first 24 h; then 4 mg/kg q12h) has been successful in some pts. AmB is not effective, but some infections have been cured with voriconazole at the doses used to treat fusariosis. In contrast to most fungi, Pneumocystis lacks ergosterol and is not susceptible to antifungal drugs that inhibit ergosterol synthesis. Developmental stages include the small trophic form, the cyst, and the intermediate precyst stage. Both airborne transmission and person-toperson transmission have been demonstrated. Other persons at risk include those receiving immunosuppressive therapy (particularly glucocorticoids) for cancer and organ transplantation; those taking biologic agents. The organisms are inhaled and attach tightly to type I cells in alveoli, although they remain extracellular. Severe disease may cause interstitial edema, fibrosis, and hyaline membrane formation. On physical examination, pts are found to have tachypnea, tachycardia, and cyanosis, but findings on pulmonary examination are often unremarkable. Serum lactate dehydrogenase levels can be elevated, but this finding is nonspecific. Chest x-ray classically reveals bilateral diffuse infiltrates beginning in the perihilar regions. Methenamine silver and other cell wall stains selectively stain the wall of Pneumocystis cysts. Secondary prophylaxis is indicated for all pts who have recovered from pneumocystosis. Pathogenesis · Female anopheline mosquitoes inoculate sporozoites into humans during a blood meal. After progressively consuming and degrading intracellular proteins (principally hemoglobin), trophozoites become schizonts. With repeated exposure to malaria, a specific immune response develops and limits the degree of parasitemia. Genetic disorders more common in endemic areas protect against death from malaria.