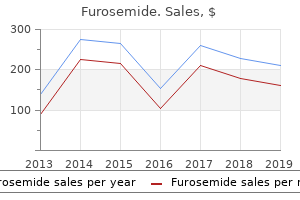
"Discount furosemide 100 mg with visa, arteria femoralis communis".
By: G. Mirzo, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of California, San Diego School of Medicine
Exposure to excess glucocorticoids alters dendritic morphology of adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons blood pressure by age order 100mg furosemide overnight delivery. Exposure to excess glucocorticoids alters dendritic morphology of the adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons hypertension synonym cheap 40mg furosemide with amex. Enduring effects of chronic corticosterone treatment on spatial learning heart attack zing mp3 generic furosemide 100 mg line, synaptic plasticity jnc 07 hypertension effective furosemide 40mg, and hippocampal neuropathology in young and mid-age rats. Chronic stress-induced acceleration of electrophysiologic and morphometric biomarkers of hippocampal aging. Glucocorticoidinduced impairment in declarative memory performance in adults humans. Decreased memory performance in health humans induced by stress-level cortisol treatment. Effects of acute prednisone administration on memory, attention and emotion in healthy human adults. Stress-and treatment-induced elevations of cortisol levels associated with impaired declarative memory in healthy adults. The effects of chronic administration of hydrocortisone on cognitive function in normal male volunteers. Effects of a single dose of cortisol on the neural correlates of episodic memory and error processing in healthy volunteers. A meta-analytic review of the effects of acute cortisol administration on human memory. Neuropsychological impairment in major depression: its nature, origin and clinical significance. Deficits in hippocampus-mediated Pavlovian conditioning in endogenous hypercortisolism. Endogenous glucocorticoids are essential for maintaining prefrontal cortical cognitive function. Selective corticosteroid antagonists modulate specific aspects of spatial orientation learning. Blockade of the mineralocorticoid receptor in healthy men: effects on experimentally induced panic symptoms, stress, hormones, and cognition. The chapter additionally addresses treatment implications, concluding with family and social considerations. Factor analytic studies, however, suggest that a four-factor solution in which avoidance symptoms are separated from numbing and other symptoms may be more appropriate [8, 9]. Rates of comorbid major depression are likewise high, typically ranging from 30 to 50% (see [18]), with rates as high as 77% in treatment-seeking populations [22]. Although some health problems may result from health risk behaviors such as increased tobacco use [28], as described below, others may be a direct consequence of neurobiological alterations. Although this response often serves an adaptive function in the immediate context of danger by facilitating actions that promote survival. This sensitization in turn can lead to over-responsiveness to subsequent stress and fear cues. Over time, the cumulative biological strain produced by repeated stress responses, known as "allostatic load," [36] can accelerate pathophysiology, including neuroimmune suppression and possibly neuronal damage. In short, the combined dysregulation of these systems is thought to result in dampened prefrontal and hippocampal functioning and reduced medial prefrontal inhibition of the amygdala, a limbic structure central to fear-based emotion. Moreover, hippocampal volumetric differences may not become apparent until adulthood (see [43] for a review) and are not necessarily associated with neurocognitive performances, including on tasks of learning and memory [57]. In children, intellectual performance decrements have been associated with both early trauma exposure [98] and cortisol-induced neuronal loss associated with trauma exposure [55].
Other related compounds have been used for the treatment of obesity though this is now discouraged: phenmetrazine (Preludin) blood pressure medication names starting with c purchase furosemide with a mastercard, diethylpropion (Apisate) blood pressure log printable generic furosemide 100mg without a prescription, phentermine (Duromine) arrhythmia consultants of connecticut order furosemide australia. Many patients have become dependent as a result of careless prescribing heart attack would feel like a heart attack purchase 100mg furosemide free shipping, and all drugs in the group may be abused for their stimulant and euphoriant effects. The use of methylamphetamine (Methedrine) by intravenous injection presented particular problems during the 1960s. Physical and psychological effects In whatever form they are taken the psychostimulants exert powerful stimulant and euphoriant effects, leading to increased energy and wakefulness for a time and feelings of great well-being. Nasal inhalation leads to a more gradual onset of euphoria, since vasoconstriction occurs within the nasal mucosa. While under the influence of the drug the subject shows enhanced alertness and mental acuity and feels increased confidence in social 714 Chapter 11 interchange. Cocaine is often regarded as an aphrodisiac because of the elation and disinhibition experienced, but higher doses lead to impotence and decreased sexual desire. The stimulant effect on the sympathetic nervous system leads to tachycardia, raised blood pressure, increased temperature and dilated pupils. Important effects are also exerted on the dopaminergic system, especially in mesolimbic and mesocortical areas (Thomas et al. Large doses can result in a dangerous degree of hypertension, cardiac dysrhythmias or grand mal convulsions. Adulterants by way of procaine or lidocaine increase the risk of cardiovascular complications or status epilepticus. Other toxic effects include muscle twitching, nausea and vomiting, irregular respiration and hyperpyrexia. Sudden fatalities can occur from cardiovascular complications such as myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation or cerebral haemorrhage. Persons with a congenital deficiency of pseudocholinesterase are at special hazard from even small doses since this enzyme metabolises cocaine. Severe malnutrition is common in regular abusers who often present with multiple vitamin deficiencies. The powerful local anaesthetic effect of cocaine serves to obscure pain, so that dental neglect can reach extreme degree. It was formerly thought that tolerance did not occur, based on experience of occasional recreational users of the drug. However, it is now clear that users of freebase forms can come to tolerate immense and frequently repeated doses, with adaptation to the convulsant and cardiovascular effects. It is less clear whether tolerance develops to the euphoriant properties though this is likely. Even the casual weekend user is prone to find that little is enjoyable without the drug, and progresses to more frequent and dangerous forms of administration. As the dosage increases dysphoric effects emerge in the wake of elation, with depression, irritability, anxiety and profound insomnia. Withdrawal results in a state of depression, apathy and increased appetite, with lethargy and disinterest often persisting for many weeks. Physical aspects of withdrawal include disturbed sleep patterns, tremors and muscle pain, but the major physiological disruptions seen with opiate and sedative withdrawal do not occur. The euphoria of acute intoxication, already described above, shows symptoms analogous to mania, with heightened pleasure, hyperactivity and increased speed of intellectual functioning. Disinhibition and impulsive behaviour are common, including a proneness to violence. A second stage, following withdrawal of the psychostimulant, is marked by dysphoria and can resemble major depression, with anxiety, misery, apathy and irritability occurring when psychostimulant levels are falling or in more prolonged abstinence when the addict is craving another dose. Restlessness and hostility can be prominent and alcohol or other drugs may be used to combat such phases. Distinguishing major depression from cocaine (or other psychostimulant) withdrawal can be a difficult diagnostic problem, most readily resolved by brief psychiatric admission. Cocaine and psychostimulant addiction have been associated with subtle neuropsychological impairments, particularly affecting executive and attentional processing, with diminished cognitive control leading to impulsivity (Ersche & Sahakian 2007; Garavan & Hester 2007), although these features may be associated with either inception or persistence of psychostimulant use rather than the consequence of use per se. Psychostimulant use is associated with the development of substance-induced psychotic disorder, which is a surprisingly heterogeneous category.
These authors note that the commonest lesions are complete infarctions arterial nephrosclerosis purchase furosemide online now, found in 75% of cases heart attack 6 hours discount furosemide master card, followed by lacunar infarcts and small infarcts in 50% of cases helvetic nerds - blood pressure generic furosemide 100mg otc, cystic infarcts in 25% of cases blood pressure negative feedback loop 100mg furosemide with visa, cerebral amyloid angiopathy in 10% and haemorrhages in only 2% of cases. Large infarcts, visible to the naked eye, often occur in the watersheds supplied by the major arteries and consist of a core of complete infarction surrounded by a penumbra of ischaemic tissue. Lacunae usually result from cavitating infarcts, occurring most frequently in the white matter but may result from haemorrhage. Small-vessel disease takes various forms but all involve damage to the end-arterial wall with hyalinisation, degeneration of the vascular smooth muscle and other changes indicative of arteriosclerosis. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy is the consequence of deposition of aggregated amyloid protein in or near the vessel wall, resulting in thickening and, almost certainly, loss of function. In post-mortem studies of series with dementia also, co-occurrence of pathologies is common and so in order to estimate true prevalence figures population-based pathological studies are needed. A recent meta-analysis found six such studies but these only reinforce the problems in correlating specific pathological findings with clinical syndromes (Zaccai et al. The risk factors for vascular dementia are, not surprisingly, evidence of vascular disease, especially in the brain. Past history of stroke, evidence of white matter damage on neuroimaging, hypertension, elevated cholesterol and adverse lipid profile, diabetes and some genetic variants are all risk factors in most studies (Schmidt et al. The natural history of dementia is classically described as stepwise or intermittent, especially in multi-infarct dementia. However, the clinicopathological correlation is not strong and slowly progressive dementia also occurs in people with pathological evidence of vascular dementia. What is clear is that vascular damage to the brain contributes significantly to impairment and to dementia specifically. It is clear that the separation of vascular damage into small-vessel and multi-infarct types together with cerebral amyloid angiopathy represents a true distinction, although it remains to be seen whether there are many clinicopathological correlations. As the contribution of vascular damage to dementia and as the importance of vascular risk factors becomes increasingly recognised, vascular dementia becomes an ever more important target for therapy. The frequency in different series varies somewhat from 10% to 20% and whether it is more common than vascular disease depends partly on probable selection biases in post-mortem series and partly on the definitions used for vascular dementia. Clinical features Males have outnumbered females in some but not all series, with onset typically in the sixties or seventies. Disease duration is on average approximately 10 years but with a wide range (Ransmayr 2000). The fluctuation may be day to day or even hour to hour and may be difficult to distinguish from Summary Vascular dementia is a concept in transition. The concept of vascular dementia as a separate disorder with different clinical profile, different set of risk factors and different pathol- 572 Chapter 9 delirium. Not infrequently patients have had episodes of admission to medical units for acute confusional states from which they apparently spontaneously recovered before the diagnosis was made. Functional neuroimaging suggests that visual hallucinations are particularly associated with hypometabolism in the primary visual cortex together with relatively preserved metabolism in the right temporoparietal association cortex (Imamura et al. In addition, the presence of extrapyramidal symptoms at presentation is highly predictive of Lewy body pathology (Haan et al. Rigidity and gait abnormalities are more prominent than tremor, although this can occur. Involuntary move- ments are sometimes reported, also myoclonus, quadriparesis, dysarthria and dysphagia (Burkhardt et al. Orthostatic hypotension may occur and unexplained losses of consciousness are often seen. Early indications suggested that the accuracy of the consensus diagnostic criteria in relation to post-mortem confirmation was at best modest (Lopez et al. One patient saw an express train going through his room, another gypsies climbing through the window. The fluctuating nature of such symptoms and their tendency to worsen at night suggested an acute confusional state superimposed on the dementia. Fluctuation was also observed in memory, language and visuospatial abilities; lucid periods with nearnormal memory capacity were sometimes recorded until late in the disease.
In these settings hypertension migraine order discount furosemide online, a relationship with seizure frequency is generally not found (Mendez et al arteria profunda femoris generic furosemide 40mg on line. However blood pressure chart neonates cheap 40 mg furosemide with amex, when such patients undergo temporal lobectomy blood pressure chart pdf effective 100 mg furosemide, becoming seizure-free is associated with an improvement in depressive symptoms (Reuber et al. This view has found some support from direct comparisons between epilepsy syndromes. A larger study comparing 150 patients with localisation-related epilepsy and 70 with idiopathic generalised epilepsy found higher measures of depression 342 Chapter 6 and anxiety in the former group (Piazzini & Canger 2001). However, the mean seizure frequency in those with generalised epilepsy was less than one per year, while those with partial seizures averaged six per month. This was not controlled for in the analyses and may well have confounded the results. In contrast, a number of recent studies have found similar rates of depression across epilepsy syndromes (Manchanda et al. Underlining the fact that patients with generalised epilepsy are at risk of depression, Cutting et al. Overall, outcome was favourable, with seizures completely controlled in two-thirds and 90% in full employment. Recent temporal lobectomy series have cast further doubt on the issue: most, including the largest series published to date (Devinsky et al. If there is an effect of laterality on depression in epilepsy, it must surely be a small one. No consistent relationships have emerged for other demographic and epilepsy-related variables including age, gender, age of onset or duration of epilepsy. A family history of psychiatric illness was found in 50% of patients with epilepsy and depression by Robertson et al. Adverse psychiatric reactions are well recognised with a number of antiepileptic drugs (Schmitz 1999). In most cases symptoms are mild, comprising non-specific features such as dysphoria, irritability and anxiety. Often, however, the extent to which a particular drug is associated with adverse effects is not clear until it has been in clinical use for several years. Those most frequently implicated include levetiracetam, tiagabine, topiramate and vigabatrin. Folic acid depletion may be caused by antiepileptic drugs, especially by those that induce hepatic enzymes, and is a treatable cause of depression (Froscher et al. Overall, temporal lobectomy is associated with a reduction in psychiatric morbidity, especially when seizures are abolished. However, approximately one-third of patients will suffer a short-lived episode of depression, typically accompanied by anxiety, and emotional lability arising de novo a few weeks after their operation (Ring et al. Those with a history of depression are at greatest risk but these reactions may occur in the absence of a past psychiatric history. Early recognition and treatment are important as symptoms may be severe, with a risk of suicide. On current evidence the natural history of these disorders seems to be for resolution within 6 months or so. They are equally likely to occur in those with and without seizure recurrence and appear to be a biological consequence of temporal lobe surgery. Overall, depression is undoubtedly common in people with epilepsy, especially those with poorly controlled seizures attending specialist services. For most patients, however, psychosocial factors related to poorly controlled epilepsy are undoubtedly important. In addition to the practical consequences of disability, including unemployment, dependence, social limitations and driving restrictions, epilepsy is still a stigmatised disorder. People whose epilepsy is in remission have a quality of life that is no different from the general population. For those with ongoing seizures, depression is the single most important predictor of a poor quality of life (Boylan et al. Freedom from seizures must clearly be the aim of epilepsy treatment, and the recognition and treatment of depression must be a high priority for all those involved in caring for people with epilepsy. Anxiety Anxiety arising as a direct manifestation of an epileptic discharge has been discussed in the preceding section on ictal psychiatric symptoms. In relation to interictal psychiatric disorders, anxiety and depression are probably equally common.
When mental disturbance is the most prominent feature arteria obstruida en el corazon order furosemide online pills, the patient may come first to the attention of the psychiatrist blood pressure what is normal furosemide 100mg on line. It is arrhythmias in children buy furosemide no prescription, of course blood pressure normal range for adults furosemide 40 mg line, comparatively rare for the psychiatrist to find a cerebral tumour in a patient with mental disorder. However, the converse is extremely common and many patients with cerebral tumours show pronounced mental symptoms at some time in their course. The frequency has been reported variously as 10% to virtually 100% of cases, depending on the care with which psychological symptoms are sought. Two of the larger series of tumour patients studied personally by the authors, and with psychological symptoms in mind, were those of Keschner et al. From the clinical point of view, mental symptoms are generally of little use as a guide to the location or nature of the tumour. Neurological signs are greatly superior in this regard, and neuroimaging has diminished the importance Third ventricle Pituitary region Fourth ventricle Pineal region Cerebellum/posterior fossa Cerebellopontine angle Cerebral Tumours Table 5. Tumour material has also proved disappointing for the study of the cerebral basis of mental phenomena. It is often hard to disentangle the effects of the lesion itself from remote pressure effects, circulatory disturbances or the generalised effects of raised intracranial pressure. Nevertheless, the psychological effects of cerebral tumours show many features of interest, and can occasionally be of crucial clinical importance, affecting the quality of life of the patient. Although fatigue, emotional and existential issues are common in all cancer patients, the presence of depressive symptoms was the single most important predictor of quality of life in a cohort of 73 brain tumour patients (Pelletier et al. Changes may be seen in any aspect of psychological function, and may be localised to one aspect or quite widespread. Complex psychological symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions may also appear, and the picture can be complicated by paroxysmal disorders consequent on an epileptogenic focus. Occasionally, frank psychotic illnesses are seen or more frequently stress-related disturbances occasioned by the constitution of the individual. In the exceptional case the tumour will present with psychiatric symptoms, but more usually the psychiatric symptoms accompany a tumour that is already known to be present. Fourteen patients displayed severe depression, seven excitements, and one each showed schizophrenia, an anxiety state, an obsessional disorder and hysteria. In very general terms it may be said that slow-growing tumours tend to produce changes of personality, and allow premorbid tendencies to manifest themselves; more fastgrowing tumours lead to cognitive defects, whereas the most rapid lead to acute organic reactions with obvious impairment of consciousness. Cognitive changes Disturbance of cognitive function is the most commonly noted psychological change. In minor degree it shows as diminished capacity to attend and concentrate, faulty memory and easy fatiguability. These rather subtle changes may be the first manifestation of the lesion, and sometimes provide the sole indication of disease for long periods of time. The cognitive changes may encompass changes in memory, attention, problem-solving, psychomotor speed and visuospatial functioning, among other deficits (Garofalo & Baum 2001). More severe cognitive impairment may present in the form of dementia, with slowed and concrete thinking, impoverished associations, defective judgement and obvious difficulty with memory. Speech may be slowed and incoherent, even in the absence of dysphasia and even with tumours of the nondominant hemisphere. Such changes can be steadily progressive, but more characteristically tend to fluctuate in severity from one occasion to another. Focal cognitive changes are commoner than generalised dementia as befits the focal nature of the lesion. A circumscribed amnesic syndrome may appear while other functions remain well preserved, with markedly defective memory for recent events, disorientation and even confabulation. All varieties of dysphasia can be seen, also apraxia, visuospatial defects and topographical disorder, and serve as a guide to location. Certain cognitive disturbances characteristic of tumours are considered in the following text.
Furosemide 100 mg fast delivery. Do At-Home Blood Pressure Monitors Work? OMRON Product Testing - BP786 - The Chronic Pain Guy.