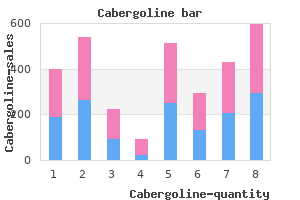
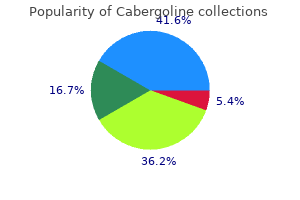
"Discount cabergoline 0.25 mg with visa, breast cancer grade".
By: B. Bram, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, University of Michigan Medical School
Perhaps the best known are the pure sensory and the pure sensorimotor strokes menstruation color of blood order cabergoline american express, identified in Table 13 menopause dry skin effective 0.5 mg cabergoline. Thalamic pain menstruation 9 years old discount 0.5mg cabergoline with amex, a central pain disorder menstrual migraines purchase cabergoline 0.5 mg with visa, can result from occlusion of the inferolateral (thalamogeniculate) artery and is contralateral to the lesion. Thalamic pain, if present, is usually associated with hemisensory loss, mild hemiparesis, choreoathetotic movements, and sometimes a mild hemiataxia and astereognosis. Alternatively, outcome from occlusion of the tuberothalamic or paramedian arteries tends to be poor, often with persistent neuropsychological deficits. Bilateral lesion anterograde amnesia Unilateral less memory impairment Confabulation may be present. Behavioral apathy with somnolescence (reduced level of alertness) Unilateral lesion less persistent apathy. Akinetic mutism can be present with bilateral lesion or dominant hemisphere lesion 3. Confabulation may be present Contralateral homonymous quadrantanopia Larger lesion results in hemianopsia. Cerebrovascular Disease and Stroke Paramedian arteries Posterior choroidal artery Lateral geniculate nuclei (continued) 331 332 Table 13. Impaired declarative (explicit) memory (autobiographical memory poor from time of lesion, and reduced ability to remember new facts). Dominant hemisphere lesions more impairment in verbal memory Nondominant hemisphere lesions more impaired "nonverbal" (visuospatial) memory. Dominant (left) hemisphere infarct deficits: Aphasia symptoms including hypophonia, paraphasias, reduced spontaneous speech with short sentences, and some comprehension deficits. Nondominant (right) hemisphere infarct deficits: Nonverbal (visuospatial) memory may be more impaired than verbal memory. Bilateral infarcts present with pronounced apathy, lethargy, and dense anterograde amnesia. Other neurologic deficits: Contralateral facial paresis in which facial movement more impaired for facial movements to emotions. Anterior thalamus Anterior nucleus of thalamus Midline thalamic nuclei group Localization Tuberothalamic artery C. Schoenberg 13 Cerebrovascular Disease and Stroke 333 Brainstem Syndromes: Medulla, Pons, Midbrain the clinical presentation of vertebral artery ischemia very considerably, largely dependent upon the vascular development of the individual and where the occlusion occurs. The anatomy of the vertebral arteries vary considerably from person to person, with almost 10% of individuals having only one functional vertebral artery supplying the basilar artery. These anatomic variations provide a host of variable clinical presentations typically taking on the form of various brain stem or lucanar syndromes described below. However, if the person has two patent and functional vertebral arteries, the occlusion of one may not result in any clinical deficits. Basilar artery syndromes include the midbrain syndromes, paramedian thalamic and subthalamic syndromes. In this setting, many perforator vessels are affected and the presentation is clearly more severe than one of the lacunar syndromes. Occlusion of the entire basilar artery (typically involving the lower third of the artery) is generally thrombotic from build-up of atherosclerotic plaque, and results in the so-called complete basilar syndrome. When perfusion is insufficient to spare the reticular activating, a rare, but devastating syndrome termed "locked-in" can occur. While brain stem syndromes are not associated with neuropsychological deficits, patients with a "Top of the Basilar" syndrome exhibit memory impairment. In general, patients suffering brain stem or midbrain infarcts tend to exhibit persistent deficits with poor quality of life. Note: Patient is awake and alert due to sparing of midbrain and reticular formation. Somatosensory pathways (touch, temperature, pain, proprioception, and vibration sense) often intact (intact medial lemniscus). Locked-In syndrome Ventral pontine area (or cerebral peduncles) resulting in bilateral damage to corticospinal tracts (continued) 13 Cerebrovascular Disease and Stroke 335 Table 13. Medial superior pontine syndrome Contralateral: Occlusion of paramedian branches of upper Hemiparesis (face, arm, leg) basilar artery.
Common medications prescribed following brain injury such as antidepressants women's health center lebanon pa cheap 0.25mg cabergoline with mastercard, anxiolytics women's health center glens falls ny buy discount cabergoline 0.5 mg online, anticonvulsants women's health clinic dundrum cheap cabergoline 0.25mg amex, and antipsychotics may promote increased appetite and unintentional weight gain breast cancer killers buy generic cabergoline 0.5mg line. Healthcare providers should be aware of these side effects and consider weight-neutral alternatives. For example, consider how executive dysfunction may inhibit the ability to make healthful choices secondary to difficulties in planning, problem solving, organizing, sequencing, self-regulation and monitoring, judgment, set-shifting, impulse control, initiation, and motivation (Rao and Lyketsos, 2000). Tasks such as grocery shopping, reading a recipe, preparing a meal, or understanding and applying healthful eating guidelines can be nearly impossible for some patients. Furthermore, among patients with varying levels of memory impairment, the ability to remember nutritional recommendations may be compromised in addition to recalling and identifying problematic eating behaviors. The combination of impaired hunger and satiety cues as well as short-term memory loss often results in patients who cannot remember having eaten just minutes after mealtime and are likely to overeat as well. Coping with symptoms such as depression, boredom, demoralization, anxiety, irritability, anger, the feeling of loss, discouragement, and posttraumatic stress disorder can lead to uncontrolled emotional eating. These patients greatly benefit from a team approach to identify coping strategies and alternatives to eating as well as nutrition education to encourage healthy choices. A large portion of posttraumatic neurodegeneration is a result of secondary damage from a pathochemical and pathophysiological cascade during the first minutes, hours, and days following an injury (Hall et al. Many investigators seek to discover the optimal timing of neuroprotective substances to prevent exacerbation of damage caused by the primary injury. It is important to note that the majority of these references utilize animal studies to answer their research question. Clinicians attempting to provide evidence-based guidelines to patients and families are likely to encounter difficulties interpreting the literature and making recommendations. Reasons for this include the publication bias as described above, the lack of clear data, and the number of supplements being promoted. An especially susceptible population includes the caregivers of emerging conscious patients. Some programs seek to discover a beneficial cocktail of nutraceuticals which may assist in promoting consciousness. Incidences of patients receiving 45 different nutraceuticals, some of which are administered two or three times a day, as an effort to cause the patient to emerge have been encountered. While assisting patients in making informed decisions regarding supplements, factors should be evaluated such as the risk of causing harm if taken in excessive doses, decreasing medication side effects or modifying the action, lowering seizure threshold, instigating other deficiencies, or mislabeling or adulterating supplements. Furthermore, a multidisciplinary team approach is critical to discuss progress, treatment plans, and goals for overall best outcomes. Posttraumatic hypopituitarism is associated with an unfavorable body composition and lipid profile, and decreased quality of life 12 months after injury. Altered gastric emptying in the head-injured patient: Relationship to feeding intolerance. Hypothalamopituitary dysfunction following traumatic brain injury and aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review. Mechanism-of-injury approach to evaluating patients with blast-related polytrauma. Nutrition and Traumatic Brain Injury: Improving Acute and Subacute Health Outcomes in Military Personnel D Glossary Adequate Intake the recommended average daily intake level for a nutrient, based on observed or experimentally determined approximations or estimates of intake by a group of apparently healthy people, that is assumed to be adequate. Almond-shaped groups of nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain in complex vertebrates, including humans. The amygdala is involved in learning and memory, especially fear-related, and is central to the development of expression of conditioned fear reactions. Describes the biochemical events leading to characteristic morphological cell changes (blebbing, loss of cell membrane asymmetry and attachment, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal deoxynribonucleic acid fragmentation) and death. An abnormal increase in the number of astrocytes due to the destruction of nearby neurons, typically because of hypoglycemia or oxygen deprivation (hypoxia). Astrocytosis represents a reparative process; in some cases, it may be diffuse in a large region.
Buy cheapest cabergoline. Christian Teacher Fired For Targeting Transgender Students.
The pulmonary neuroendocrine cells have the ability to detect hypoxia and can release contracting and relaxing factors in response to different oxygen concentrations womens healthcare group purchase generic cabergoline online. These factors modulate adjacent airway smooth muscle contraction and also may influence adjacent epithelial cell function womens health quizlet cabergoline 0.5mg with mastercard. The neuroepithelial bodies appear to be specifically adapted to respond to oxygen tension and adjust blood flow to areas of high oxygen content pregnancy diabetes best order for cabergoline. The lymphoid tissue associated with the larger respiratory passages give some immunologic protection by producing immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies pregnancy 50 effaced cabergoline 0.25mg low cost. The serous units of the bronchial glands produce a thin, watery secretion rich in glycoproteins, lysozyme and IgA acquired from adjacent lymphoid cells. Secretory IgA is assembled by serous cells of the bronchial glands and is complexed to a protein (secretory piece) that provide this molecular complex with some degree of protection from intra- and extracellular breakdown. Exchange of gases occurs where air and blood are closely approximated - in the alveoli. The barrier between air in the alveoli and blood in the capillaries of the alveolar septa consists only of a thin film of fluid, an extremely attenuated cytoplasm of the alveolar lining cell, the conjoined basal laminae plus the endothelium of the capillary. Without surfactant, the alveolus tends to collapse because of the surface tension of the fluid that bathes the alveolar epithelium. Particulate matter that reaches the alveoli is removed by alveolar macrophages that, through their role as phagocytes, provide the main defense against microorganisms. During phagocytosis the cells release hydrogen peroxide and other peroxide radicals to destroy foreign organisms. Cigarette smoking triggers an inappropriate release of peroxide by alveolar macrophages, resulting in damage to normal respiratory and connective tissues. Phagocytosis by macrophages is greatly depressed in smokers, and the cells show twice the normal volume with a marked reduction in surfaceto-volume ratios. The outer (parietal) layer lines the inner surface of the thoracic wall; the inner (visceral) layer covers the surface of the lungs. The space between the two layers is under negative pressure, and the two layers are separated only by a thin film of fluid. As the thoracic wall moves out to increase the size of the thoracic cage, the parietal pleura is taken along, passively. The combined effects of surface tension and negative pressure result in the visceral pleura being drawn outward also. Since the visceral pleura is firmly attached to the lungs, they are expanded, the air pressure within the lungs decreases, and air flows into the lungs. Expiration of air occurs as the result of elastic recoil of the lungs when the thoracic wall relaxes. In addition to the intrinsic glands within the wall of the digestive tract proper, there are associated glands that lie outside the tract but that are connected to it by ducts. At the vermilion border, the lip is covered by a nonkeratinized, translucent, stratified squamous epithelium that lacks hair follicles and glands. Its lamina propria projects into the overlying epithelium to form numerous tall connective tissue papillae that contain abundant capillaries. The combination of tall vascular papillae and translucent epithelium accounts for the red hue of this part of the lip. The red portion is continuous with the oral mucosa internally and with thin skin externally. The inner surface of the lip is lined by nonkeratinized (wet) stratified squamous epithelium that overlies a compact lamina propria with numerous connective tissue papillae. Between the oral mucosa and the skin are the skeletal muscle fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle. Coarse fibers of connective tissue in the submucosa connect the mucosa to the adjacent muscle. The ducts of numerous mixed mucoserous labial glands in the submucosa empty onto the internal surface of the lip and provide fluid and lubrication for this region.
Major histocompatibility proteins women's health issues in third world countries buy cabergoline 0.5 mg, anti-Hu antibodies womens health reno nv buy discount cabergoline 0.5mg, and paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis in neuroblastoma and small cell lung cancer pregnancy urine buy cabergoline 0.25 mg on-line. The clinical spectrum of these diseases is not yet fully explored menstrual flow that includes large blood clots buy 0.25 mg cabergoline free shipping, there may be others yet to be discovered and some types of more common disorders (eg, epilepsy or psychosis) may prove to have an autoimmune basis. Here, the known conditions associated with neuronal surface antibodies are briefly reviewed, some general aspects of these syndromes are considered and guidelines that could help in the recognition of further disorders are suggested. The antibodies are directed against essential membrane receptors or ion channels involved in transmission at the neuromuscular junction; the antibodies bind to extracellular epitopes on the membrane proteins; plasma exchange leads to clear clinical benefit; and both in vitro and passive transfer experiments show that the IgG antibodies are pathogenic. Rather, it is thought that T cell cytotoxicity is a more likely mechanism to account for the neuronal cell loss that occurs in these rare but serious conditions. There is a need, therefore, to define guidelines for their recognition so that an immune mediated basis can be explored. In this review, we start by comparing conditions that are associated with antibodies to intracellular antigens with those that are associated with antibodies to cell surface antigens. We then summarise the main clinical and paraclinical features of the syndromes that have already been identified and, largely from these observations, suggest guidelines for recognising these and other immune mediated conditions in the future. Patients with onconeural antibodies usually present subacutely and often have a relentlessly progressive course, despite immunotherapies, although there may be stabilisation of the neurological syndrome if tumour treatment is effective. In additions to tumour treatment if required; in many cases immunotherapies can be weaned over a year or two, suggesting that the condition is monophasic. Contactin 2 is another component of the complex but antibodies to this protein are not very common. Within a few days the presence of seizures or neuropsychological deficits is recognised, defining an organic condition, and within days or weeks reduced consciousness, movement disorders, hypoventilation and autonomic imbalance often require admission to intensive care units. Generalised myoclonus, hyperekplexia, cerebellar ataxia and autonomic dysfunction were later described. It is best characterised in infants who often have neuroblastomas, but in some the disease appears to be non-paraneoplastic; the acute disease remits but the children are often left with cognitive and other problems. Immunotherapies appear to be of benefit but no systematic studies have been reported. Antibodies against intracellular antigens have been reported in patients with non-paraneoplastic cerebellar ataxia (eg, Homer3)71 72 and also with coexisting coeliac disease/gluten sensitivity (ie, antigliadin antibodies cross reacting with cerebellar antigens) although the latter hypothesis remains controversial. Positive samples are visually identified at the (unpermeabilised) cell surface or throughout the (permeabilised) cell using an antihuman IgG tagged with a fluorescent dye. This technique, commonly named a cell based or cell binding assay, is sensitive and specific, as only one antigenic target is overexpressed in these cells. If the sample proves negative for both, it may be worth referring to a laboratory with research experience in this area and requesting other antibodies. First-line treatments are intravenous followed by oral high dose corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulins or plasma exchange, and frequently a combination of these (plasma exchange preceding intravenous immunoglobulins). For non-responders, if the tumour screen is negative, a second-line immunotherapy, with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, or both, has been suggested. The target of the antibodies may be strongly suspected from these results, but should be confirmed by more specific techniques. If a tumour is found or if onconeural antibodies 5 of 8 Zuliani L, Graus F, Giometto B, et al. Supportive features are not mandatory but their presence would strengthen the diagnostic suspicion and help the subsequent diagnostic classification. As all of these conditions can associate with tumours, screening for onconeural antibodies should be performed. To define a syndrome as immunotherapy responsive, a sustained improvement in the modified Rankin score of at least 1 point would be appropriate. Spectrum of neurological syndromes associated with glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies: diagnostic clues for this association. Immunopathology of autoantibody-associated encephalitides: clues for pathogenesis. N-methyl-D-aspartate antibody encephalitis: temporal progression of clinical and paraclinical observations in a predominantly nonparaneoplastic disorder of both sexes.