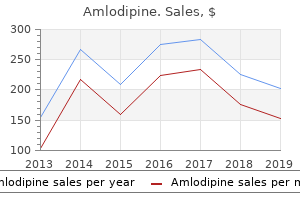
"Order amlodipine 5 mg on line, arterial network".
By: H. Hurit, M.B.A., M.D.
Medical Instructor, Frank H. Netter M.D. School of Medicine at Quinnipiac University
The patient opens the mouth blood pressure zanidip amlodipine 2.5 mg online, allowing the chin to drop blood pressure 200 100 buy amlodipine 10 mg online, and the practitioner cradles the mandible with the left hand arrhythmia ablation order amlodipine discount, so that the fingers are curled under the jaw blood pressure 3060 purchase amlodipine 10mg online. After a few seconds of gentle isometric contraction, the practitioner and patient slowly relax simultaneously and the jaw will usually have an increased lateral excursion. This method should be performed so that the lateral pull is away from the side to which the jaw deviates on opening. A central metopic suture which is usually fused but sometimes (rarely) interdigitated, on the inside of which lie the attachments for the bifurcated falx cerebri Bilateral concave domed bosses which house the frontal lobes of the brain as well as air sinuses at the inferior medial corner Superciliary arches, a nasal spine and the medial aspects of the eye socket the patient curls the tongue upwards, placing the tip as far back on the roof of the mouth as possible. While this is maintained in position, the patient slowly opens and closes the mouth (gently) to activate the suprahyoid, posterior temporalis and posterior digastric muscles (the retrusive group). Temporalis arises from the temporal fossa and its fibers converge to attach on the coronoid process and ramus of the mandible, medial to the zygomatic arch. The origin of temporalis crosses the coronal suture between the frontal and parietal bone as well as the suture between the temporal bone and the parietal. The muscle also spans the lambdoidal and coronal sutures, attaching via direct or indirect linkages with the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital bones. Frontalis merges with the superficial fascia of the eyebrow area while some fibers are continuous with fibers of corrugator supercilii and orbicularis oculi attaching to the zygomatic process of the frontal bone, with further linkage to the epicranial aponeurosis anterior to the coronal suture. Corrugator supercilii lies medial to the eyebrow and comprises a small pyramid-shaped structure lying deeper than occipitofrontalis and orbicularis oculi. Orbicularis oculi is a broad flat muscle which forms part of the eyelids, surrounds the eye and runs into the cheeks and temporal region. Procerus is a slip of nasal muscle that is continuous with the medial side of the frontal part of occipitofrontalis. Other associations and influences Associations with problems of the eyes and sinuses are clear from the geography of the region alone and congestion and discomfort in this area can at times be related to frontal bone compression or lack of freedom of motion. The connection with the falx cerebri offers other possible linkages, in particular to cranial circulation and drainage. Dysfunctional patterns Apart from direct blows to the forehead, few problems seem to arise as a direct result of frontal dysfunction. However, as with the parietals (see below), problems may arise as a result of the accommodation of the bone to influences on it, temporal, parietal, sphenoidal, or from the facial bones. As the patient exhales the interlaced hands exert light compressive force to take out slack (grams only) via the hypothenar eminences (bringing them toward each other), utilizing a very slight contraction of the extensor muscles A B Figure 12. At the same time a slight upwards (slightly cephalad and toward the ceiling) lift is introduced bilaterally to release the frontal bone from its articulations with the parietals, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillae and zygomae. This lift is held during several cycles of inhalation and exhalation, after which the frontal bone is allowed to settle back into its resting position. Reciprocal tension membrane relationships the falx cerebri attaches strongly into a groove on each side of the sagittal suture forming a space that is the superior Superior temporal line Inferior temporal line Parietal tuberosity Articulates with frontal bone Articulates with occipital bone A Articulates with greater wing of sphenoid bone Articulates with squamous part of temporal bone Articulates with mastoid part of temporal bone Groove for superior sagittal sinus Frontal angle Articulates with opposite parietal bone Occipital angle Groove for sigmoid sinus Sphenoidal angle Mastoid angle B Groove for parietal branch of middle meningeal vessels Groove for frontal branch of middle meningeal vessels Figure 12. The origin of temporalis crosses the coronal suture as well as that between the temporal bone and the parietal. Auricularis superior is a thin, fan-shaped muscle that arises from the epicranial aponeurosis, converging to insert by a flat tendon into the upper surface of the auricle. Occipitofrontalis does not attach directly to the parietals although its aponeurosis covers them. Range and direction of motion Human studies indicate that approximately 250 microns of movement is available at the sagittal suture (Lewandowski & Drasby 1996). There is a greater degree of interdigitation on the posterior aspect of the sagittal suture where motion potential is therefore greatest. A more pragmatic view is that the pliability of the suture helps to absorb stresses imposed on the structure via either internal or external forces (Chaitow 2005). The other finger pads rest on the parietal bone just above the temporoparietal suture so that the middle finger is approximately one finger width above the helix of the ear, on the parietal bone (not the temporal). The thumbs act as a fulcrum, bracing against each other or crossed above the sagittal suture without any direct contact.
In the crying infant blood pressure medication that starts with t discount amlodipine 10 mg line, it may be extremely difficult to coordinate the timing of the film exposure with expiration; in these circumstances blood pressure tracker order amlodipine 5mg otc, bilateral decubitus films can be ordered arrhythmia practice strips buy 10mg amlodipine otc. A serious condition determination was made if two or three of the panel members felt the infant had a condition that required prompt treatment or had the potential for harm if the condition was not recognized and treated arrhythmia is another term for order amlodipine pills in toronto. Special attention should be paid to the diagnosis of infant colic (paroxysmal fussiness, infantile colic, evening colic, 3-month colic). In addition, the "skeletal survey" is useful to look for signs of previous trauma. A spiral fracture courses from the distal portion to the upper third of the diaphysis. An echocardiogram can also provide information about structural and flow abnormalities of the heart. Hypoglycemia in the infant is often associated with sepsis, errors of metabolism, and certain toxic ingestions. Electrolytes Serum electrolytes may be indicated in the evaluation of a crying infant to look for hyper- or hyponatremia, hyper- or hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis, and hypocalcemia. Urinary tract infections are common in infants, particularly girls younger than 12 months, boys younger than 6 months, and uncircumcised boys younger than 12 months. Lumbar puncture A lumbar puncture with cell count and differential, Gram stain, glucose and protein determination, and culture should be performed if meningitis is suspected as the cause of inconsolable crying. This study provides information about brain injuries (contusions and hematomas) as well as most skull fractures. It may also be helpful in diagnosing hydrocephalus or other congenital abnormalities. An inconsolable crying infant may have to be sedated and closely monitored in order to obtain this study. It is important, however, that indicated studies be obtained regardless of the need for sedation and monitoring, and the increase in work that such diagnostic tests cause. Barium enema A barium or air-contrast enema is indicated when concerns for intussusception must be answered. These tests are not only diagnostic but often therapeutic, reducing the intussusception. Consultation with a pediatric surgeon and radiologist are warranted prior to the study in the case that emergent surgical intervention is necessary. Abdominal ultrasonography has a role in the diagnosis of intussusception, depending on the skill of the radiologist. Toxicologic screening may be indicated in infants where acute or chronic exposures are considered. Liver enzymes Liver transaminases and bilirubin may be used as a screening test for liver injuries associated with blunt abdominal trauma. Amino and organic acid studies Amino and organic acid studies may be ordered in cases in which an inborn error of metabolism is suspected. Crying and irritability General treatment principles There is no single medication that can be recommended for the crying infant because of the large variety and spectrum of etiologies responsible. Disposition the disposition of the infant with persistent crying and irritability will likely be dictated by the ultimate diagnosis. If there are concerns about parental reliability or safety, the child is best admitted to the hospital. Special patients Infants who were premature or are immunocompromised are at special risk for infectious etiologies as the cause of inconsolable crying. Pearls, pitfalls, and myths · Ask about medication use, including over-thecounter medications and medications used Primary Complaints 223 · · · · · · · · · by a breast-feeding mother. This should include topical medications that a breastfeeding mother may apply to her nipples. The diagnosis of excessive crying should be made using a process of elimination, after ruling out the more dangerous causes.
Purchase amlodipine cheap online. 4 Essential Oils for Anxiety.
The medial vermis pulse pressure definition medical buy amlodipine now, via the fastigial nucleus prehypertension triples heart attack risk cheap amlodipine 2.5 mg amex, projects to nuclei of origin of reticulospinal pathways involved in locomotion and medial vestibulospinal pathways involved in head-eye coordination arteria3d purchase amlodipine without a prescription. The lateral vermis projects directly to the lateral vestibular nucleus blood pressure pills joint pain cheap amlodipine uk, which gives rise to the vestibulospinal tract, which is critical for maintenance of posture against gravity. The intermediate cerebellum (paravermis) receives information about the progress of limb movements from peripheral receptors via the dorsal spinocerebellar and cuneocerebellar tracts, about excitability of spinal interneurons via the ventral spinocerebellar tract, and about cortical motor commands via the pontine nuclei. Through these connections, the intermediate cerebellum controls the motor pathways that project to the motoneurons innervating the more distal portions of the limbs and digits. Chapter 17, Basal ganglia and cerebellum: functional organization and role in control of motor and cognitive behavior; p. From the ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus, axons project to the motor and premotor cortices. The dentate discharges and provides a trigger signal to the motor cortex and initiates a movement with a sensory stimulus. This stimulus allows the dentate to aid in specification of the direction, timing, intensity, and pattern of muscle use. Ocular Motor Circuitry the vestibulocerebellum (flocculus, paraflocculus, and nodulus) is important in the vestibuloocular reflex and smooth pursuit (Figure 18. Efferent axons from the flocculus and paraflocculus project back to the medial vestibular nuclei and then to the cranial nerve nuclei involved in ocular movement. Dysfunction of this pathway may result in saccadic pursuit and gaze-evoked nystagmus. The dorsal vermis receives input from the paramedian pontine reticular formation (excitatory burst neuron Chapter 18. Purkinje cells of the dorsal vermis discharge before the contralateral saccades and project to the fastigial nuclei. The fastigial nuclei then project axons to the contralateral brainstem premotor burst and omnipause neurons controlling saccades (Figure 18. Dysfunction along this pathway may result in saccadic dysmetria and sometimes opsoclonus. Cognitive and Limbic Circuitry There are many reciprocal interconnections of the cerebellum with areas of the cortex, particularly the prefrontal 162 Section I. The main function of the flocculonodular lobe and adjacent uvula and ventral paraflocculus (vestibulocerebellum) is the control of eye movements. The flocculus and paraflocculus project to the medial and superior vestibular nuclei, which control eye movements, including the horizontal and vertical vestibuloocular reflexes and smooth pursuit. Information descends via the pontine nuclei and returns via the ventral dentate to the same cortical region. In functional brain imaging studies, the lateral aspect of the posterior lobe of the cerebellum appears to be important for language, verbal working memory, spatial tasks, executive function, and emotional processing. The limbic circuitry involves the vermis of the posterior lobe and the fastigial nucleus. The posterior or dorsal vermis, via the fastigial oculomotor region, controls the amplitude, direction, and velocity of saccadic eye movements. These structures receive inputs from the pontine paramedian reticular formation, which contains the excitatory burst neurons for horizontal saccades, and from the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis, which relays saccadic signals from the frontal eye fields and superior colliculus. The fastigial nucleus projects to the saccadic burst generator of the brainstem via the uncinate fasciculus and controls the amplitude of ipsilateral and contralateral saccades. If the inputs do not match, an increase in firing of the inferior olivary nucleus results in an error signal. The role of the inferior olive may be to provide a timing signal to the cerebellum, and the inferior olive may contribute to detection and correction of errors in motor performance. Neurons of the inferior olivary nucleus project a low-frequency, synchronized oscillatory activity via the 164 Section I. Neuroscience and Neuroanatomy disorders resulting in cerebellar findings or ataxia, see Volume 2, Chapter 26, "Cerebellar Disorders and Ataxias.
Accumulation of misfolded proteins or damaged organelles is a common apoptotic trigger pulse pressure pv loop purchase discount amlodipine. Which of the following statements regarding neurotransmitter receptor mechanisms is most correct? Targets for drug action and a basis for understanding how medications exert their action are also discussed pulse pressure amplification order amlodipine 10 mg without a prescription. Principles of Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetic principles of neurologic medications are important to understand for the purposes of medication prescribing and ordering (Figure 27 arrhythmia journal articles buy generic amlodipine 5mg on-line. Multiple routes of administration-intravenous blood pressure medication for young adults effective amlodipine 2.5mg, sublingual, intramuscular, subcutaneous, rectal, oral, and transdermal-are available for neurologic therapeutic agents. Oral administration is affected by gastric pH, gastric contents, gastric emptying time, transmembrane transport mechanisms, and gastrointestinal tract motility. These factors can be altered by medication coadministration, medical conditions, and age. The volume of distribution is the ratio of total amount of drug in the body to drug blood plasma concentration and reflects how the drug will be distributed throughout the body per dose, based on a number of parameters. The expected serum concentration (Co) after the administration of a specific dose (D) is calculated using the volume of distribution (Vd): Co = D/Vd. Understanding the volume of distribution is important in order to predict duration of drug effect for certain drugs. As a result, a bioequivalent dose of diazepam has a shorter duration of anticonvulsant action than lorazepam as it is effectively diluted by its wide distribution after administration. Factors affecting volume of distribution include body mass, body fat percentage, solubility, and protein binding. Serum proteins that bind drugs include albumin, lipoprotein, glycoprotein, and -, -, and -globulins. Protein binding is impacted by factors intrinsic to the drug and by serum protein concentration. The latter is affected by age, concurrent illnesses, and other medications taken by the patient (Box 27. Neurologic drugs in which serum protein binding plays an important clinical role include phenytoin, valproic acid, and carbamazepine. Use of serum-free concentrations in monitoring therapy is important with use of these drugs in patients in whom serum protein binding is affected. Hepatic metabolism of neurologic therapeutics is primarily through the cytochrome P-450 and uridineglucuronyl transferase enzyme systems. Lipid-soluble molecules are able to cross the blood-brain barrier relatively easily, while water-soluble molecules are often unable to cross the barrier or require the assistance of transport channels. The integrity of the blood-brain barrier is maintained by tight junctions between endothelial cells in the capillaries, choroid plexus, and the meninges. These tight junctions limit the passage of compounds in either direction, particularly for large and water-soluble molecules. Neuropharmacology 239 · Pharmacokinetic principles of neurologic medications · are important to understand for the purposes of medication prescribing and ordering. Lipid-soluble molecules are able to cross the bloodbrain barrier relatively easily, while water-soluble molecules are often unable to cross the barrier or require the assistance of transport channels. Major Neurologic Targets the functions of the neurologic system depend on signaling across synapses and axonal propagation, which allow communication between different brain regions in neural networks. Synaptic and axonal propagation mechanisms provide the target for many neurologic therapeutic agents. After glutamate is released into the synapse, it is taken up into glial cells by excitatory amino acid transporters and converted into glutamine by glutamine synthetase. The bidirectional conversion between glutamate and glutamine allows for rapid neurotransmission. Glutamate acts on a number of ionotropic and metabotropic glutamatergic receptors. When glutamate binds to one of these receptors, the channel opens, allowing Ca2+ and Na+ influx to the postsynaptic terminal, resulting in depolarization. Glutamatergic pathways are important in the mechanisms of seizures and long-term potentiation underlying memory formation. Ion Channels Electrical signals in the nervous system are propagated by alterations in the resting membrane potential, which is determined by the relative balance of the fluxes of sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), chloride (Cl-), and calcium (Ca2+) across the membrane.